Discover the ultimate guide to unlocking the benefits of the world’s most versatile superfood powder. Learn how to seamlessly integrate this nutrient-packed powerhouse into your daily routine for enhanced health and well-being. Perfect for health enthusiasts seeking to elevate their diet.
Introduction
Moringa Oleifera, often hailed as the “Miracle Tree,” is making waves for its superfood qualities. Packed with vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, moringa powder is a versatile addition to any diet. Let’s dive into why this plant is gaining popularity and how you can incorporate it into your daily routine.
What is Moringa?
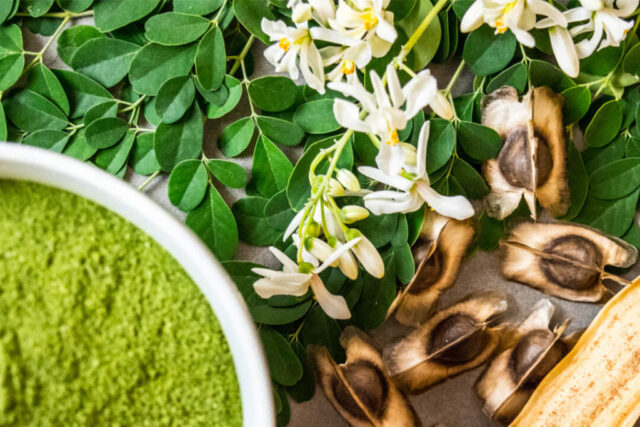
Moringa, scientifically known as Moringa oleifera, is a highly valued plant native to parts of Africa and Asia, known for its remarkable nutritional and medicinal properties. Often referred to as the “drumstick tree,” “miracle tree,” or “horseradish tree,” Moringa has been used for centuries in various cultures for its health benefits.
The moringa tree is drought-resistant and fast-growing, making it an invaluable resource in regions where malnutrition and food scarcity are prevalent. Almost every part of the moringa tree can be used for food or has some other beneficial property. The leaves, pods, seeds, flowers, roots, and bark of the tree are all utilized for their health-promoting qualities.
Nutritional Profile: Moringa leaves are incredibly nutritious; they are a rich source of vitamins A, C, and E, calcium, potassium, and protein. The leaves contain all the essential amino acids required for human growth and development. Compared to common foods, moringa leaves often have higher concentrations of nutrients. For example, they contain more vitamin C than oranges, more potassium than bananas, more calcium than milk, and more iron than spinach.
Health Benefits: The consumption of moringa has been linked to various health benefits, including:
- Boosting the immune system: The high antioxidant content helps fight free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
- Enhancing energy levels: With its rich iron and vitamin A content, moringa helps in improving metabolic functions and energy levels.
- Supporting brain health: The antioxidants and neuro-enhancer activities of moringa may help in improving brain health and cognitive functions.
- Promoting heart health: Moringa has been found to possess properties that help in lowering blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels, contributing to heart health.
- Aiding digestion: The fiber content in moringa leaves can help in maintaining a healthy digestive system.
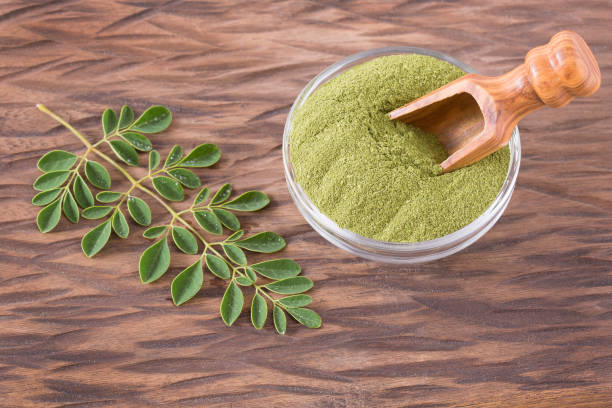
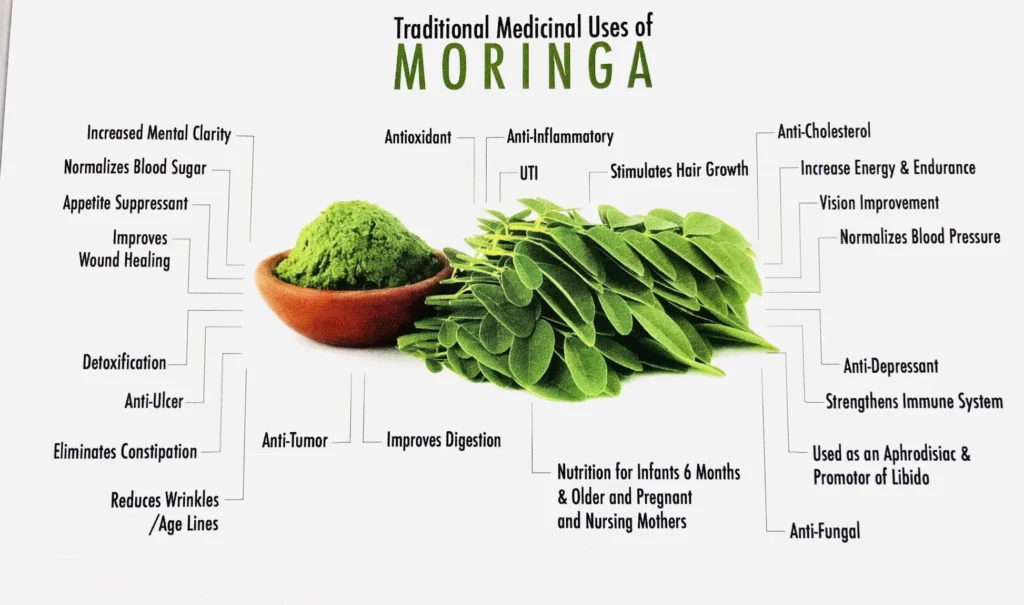

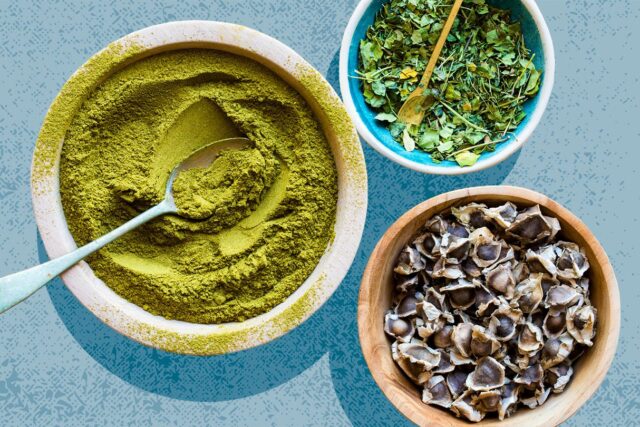
Usage: Moringa can be consumed in various forms; the leaves can be eaten fresh, cooked, or dried and powdered for use as a dietary supplement. The powder can be added to smoothies, soups, and teas, or used as a seasoning in a variety of dishes. The seeds can be eaten like nuts or used to purify water due to their coagulating properties.
History of Moringa
Ancient Uses and Cultural Significance:
- Ayurvedic Medicine: Moringa is most notably mentioned in ancient Ayurvedic texts, dating back over 4,000 years. In Ayurveda, it was believed to prevent and cure over 300 diseases, highlighting its value in one of the world’s oldest holistic healing systems.
- Ancient Egypt: Egyptians prized Moringa oil, extracted from its seeds, for its nourishing skin properties and used it in making perfumes and protecting their skin from the harsh desert climate. Moringa oil was also placed in tombs for use in the afterlife.
- Traditional African and Asian Medicine: In various African and Asian cultures, Moringa was used to treat a plethora of ailments ranging from malnutrition to infectious diseases and chronic conditions such as diabetes.
- Greco-Roman World: The Greeks and Romans recognized Moringa for its therapeutic properties and utilized the oil extensively for cosmetic and pharmaceutical purposes.

Spread and Global Recognition:
The versatility and resilience of the Moringa tree allowed it to be easily cultivated in many parts of the world. Its ability to grow rapidly and withstand harsh conditions made it an ideal candidate for addressing malnutrition and providing food security in many developing countries.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, Moringa has gained global recognition as a “superfood” due to its dense nutritional profile. Scientific research has begun to validate many of the traditional uses of Moringa, studying its potential benefits in health and wellness, water purification, and even as a sustainable energy source.
Modern Usage:
Today, Moringa is cultivated worldwide for its leaves, pods, seeds, and oil. The global health and wellness community has embraced Moringa for its high concentration of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It is marketed in various forms, including powders, pills, teas, and oils. Beyond its health benefits, Moringa is also being explored for its environmental and agricultural applications, such as a natural pesticide, a means of water purification, and a sustainable biofuel.
Nutritional Profile
Vitamins
- Vitamin A (Beta-Carotene): Moringa leaves are rich in beta-carotene, an antioxidant that converts to vitamin A in the body, essential for healthy skin, vision, and immune function.
- Vitamin C: With a high vitamin C content, Moringa boosts the immune system, aids in the absorption of iron, and helps repair tissues.
- Vitamin E: Moringa’s vitamin E content acts as a potent antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress.
Minerals
- Calcium: The leaves contain high levels of calcium, vital for bone health, muscle function, and nerve signaling.
- Potassium: Moringa leaves are rich in potassium, necessary for maintaining normal blood pressure, fluid balance, and heart function.
- Iron: High in iron, Moringa helps in the formation of hemoglobin and red blood cells, reducing the risk of anemia.
- Magnesium: Essential for over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, magnesium in Moringa supports muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and energy production.
Proteins and Amino Acids
- Moringa leaves are an excellent source of protein, particularly important for vegetarians and vegans. They contain all nine essential amino acids, making it a rare plant-based source of complete protein.
Antioxidants
- Moringa leaves are packed with antioxidants such as quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and beta-carotene. These compounds fight free radicals, molecules that cause oxidative stress, cell damage, and inflammation.
Fiber
- The high fiber content in Moringa leaves aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut by preventing constipation and supporting regular bowel movements.
Other Compounds
- Zeatin: Moringa contains zeatin, a plant hormone that supports cellular growth and delays aging of cells.
- Isothiocyanates: These are compounds known for their anti-inflammatory properties and are studied for their potential role in reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.

Health Benefits
1. Boosts Immune System
Moringa is high in vitamin C, which is essential for the immune system’s function. It helps stimulate the production of white blood cells and acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
2. Rich in Antioxidants
The leaves of the Moringa tree contain a variety of powerful antioxidants, such as quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and beta-carotene. These compounds can help prevent oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and cancer.
3. Promotes Heart Health
Moringa has been found to have heart-healthy benefits, including reducing high blood pressure, cholesterol, and formation of plaques in the artery walls. This can lower the risk of heart disease.
4. Supports Brain Health
The antioxidants and neuroprotective properties of Moringa may support brain health. It can enhance cognitive function by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and by combating neurodegeneration.
5. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Moringa contains isothiocyanates, which are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Chronic inflammation is linked to many health issues, including heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. By reducing inflammation, Moringa can help protect against these conditions.
6. Improves Digestive Health
The fiber content in Moringa leaves aids in digestion and can help prevent constipation, supporting a healthy digestive system.
7. Enhances Energy Levels and Physical Performance
Despite being low in calories, Moringa is rich in vitamins and minerals that can boost energy levels and improve physical stamina. It is particularly beneficial for athletes or anyone needing an energy uplift without the jitters associated with caffeine.
8. Supports Weight Loss
Moringa can aid in weight loss and weight management. Its leaves are low in fat and high in beneficial nutrients, making it a nutritious addition to a weight-loss diet. The high fiber content also helps keep you full longer, reducing the urge to snack.
9. Regulates Blood Sugar Levels
Moringa has been shown to help regulate blood sugar levels, which can be beneficial for people with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. The chlorogenic acid found in Moringa leaves can help moderate blood sugar levels after meals.
10. Improves Skin and Hair Health
Rich in vitamins A and E, Moringa can improve skin health by promoting collagen production, reducing fine lines and wrinkles, and combating oxidative stress that leads to skin aging. Its nutrients also support healthy hair growth and maintenance.
11. Bone Health
Moringa’s high calcium and phosphorus content helps keep bones healthy and strong. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties can reduce symptoms of arthritis and other bone-related diseases.
12. Detoxification
Moringa has detoxifying properties, thanks to its ability to purify water and remove impurities from the body. It supports liver function and can help cleanse the body of toxins.

How to Use Moringa Powder
1. Smoothies and Juices
Adding a teaspoon or two of Moringa powder to your smoothies or juices is an excellent way to increase your intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Its mild taste pairs well with fruits and vegetables, boosting the nutritional profile of your drink.
2. Teas and Infusions
Stir a half teaspoon of Moringa powder into a cup of hot water to make a simple Moringa tea. You can also add it to your favorite herbal teas to enhance their health benefits.
3. Soups and Stews
Moringa powder can be added to soups and stews just before serving. It enriches the dish with nutrients without altering the flavor significantly. Start with a small amount and adjust according to taste and nutritional needs.
4. Baked Goods
Incorporate Moringa powder into your baking recipes, such as bread, muffins, or pancakes. Adding a tablespoon of Moringa powder to the dough or batter can increase the nutritional content of your baked goods. It can also give them a lovely green hue.
5. Salad Dressings
Mix Moringa powder into your salad dressings or sprinkle it directly onto salads. It’s an easy way to add a healthful boost to your fresh vegetables.
6. Energy Bars and Balls
For a nutritious snack, include Moringa powder in your homemade energy bars or balls. Combine it with ingredients like nuts, seeds, dried fruits, and honey for a healthy, energizing treat.
7. Yogurt and Oatmeal
Stir Moringa powder into your morning yogurt or oatmeal. It adds vitamins and minerals to your breakfast, starting your day on a nutritious note.
8. Sauces and Pesto
Incorporate Moringa powder into sauces, pesto, or dips. Its green color and health benefits make it an excellent addition to green pesto, hummus, or guacamole.
Tips for Using Moringa Powder
- Start Small: If you’re new to Moringa, begin with a small amount (such as a teaspoon) to see how your body reacts, and gradually increase the quantity.
- Heat Sensitivity: While Moringa powder can be cooked, excessive heat may reduce some of its nutritional value. Consider adding it towards the end of the cooking process or using it in no-cook recipes.
- Taste Adjustment: Moringa has a distinctive taste that some may need to get used to. Pairing it with strong flavors like citrus, ginger, or honey can help mask its taste while you adjust.

Buying and Storing Tips
Buying Tips
1. Source: Look for Moringa products from reputable sources. Organic certification can be a good indicator of quality, as it ensures the product is grown without harmful pesticides or chemicals.
2. Form: Moringa is available in several forms, including powder, capsules, tea, and oil. Choose the form that best suits your needs and preferences. Moringa powder is versatile for cooking and smoothies, while capsules might be convenient for those constantly on the go.
3. Packaging: Pay attention to the packaging. Moringa should be packaged in airtight containers to protect it from moisture and preserve its nutritional content. Avoid products that seem to have been exposed to air, light, or moisture.
4. Color and Smell: High-quality Moringa powder should have a vibrant green color and a fresh, earthy smell. Any signs of dullness or an off-odor can indicate poor quality or that the product has gone bad.
5. Expiration Date: Always check the expiration date to ensure you’re buying a fresh product. Consuming Moringa past its expiration date can reduce its nutritional benefits.
Storing Tips
1. Keep it Dry: Store Moringa in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Moisture can lead to spoilage and decrease its shelf life.
2. Airtight Containers: Whether it’s powder, seeds, or leaves, Moringa should be stored in airtight containers to prevent exposure to air, which can degrade its quality over time.
3. Refrigeration: While not always necessary, storing Moringa powder in the refrigerator can help preserve its freshness and extend its shelf life, especially in warmer climates.
4. Avoid Contamination: Use a clean, dry spoon every time you use the Moringa powder to avoid introducing moisture into the container.
5. Bulk Purchases: If you buy Moringa in bulk, consider dividing it into smaller portions and storing them separately. This way, you only open what you need, keeping the rest fresh.

Conclusion
Moringa is more than just a trend; it’s a nutrient-packed superfood that offers numerous health benefits. From boosting immunity to enhancing energy levels, moringa powder is a simple yet effective way to improve your overall health.
FAQs
- Is moringa safe for everyone? Yes, but it’s recommended to consult a healthcare provider if you’re pregnant or have health conditions.
- Can moringa replace my daily multivitamin? While moringa is nutrient-dense, it should complement a balanced diet rather than replace it.
- How much moringa powder should I use daily? Start with 1-2 teaspoons daily and adjust based on your needs and tolerance.
- Can I grow moringa at home? Yes, in warmer climates, moringa trees can be grown in your backyard.
- Does moringa have any side effects? Consumed in moderation, moringa has no known severe side effects but can have a laxative effect if overconsumed.



MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers