Discover the ultimate guide to understanding, treating, and managing bunions (Hallux Valgus). From symptoms to solutions, get expert advice for pain-free, healthy feet.
Introduction
Bunions, medically known as Hallux Valgus, are a common foot ailment characterized by a bony bump at the base of the big toe. This condition, resulting from joint misalignment and toe deviation, can lead to significant discomfort and mobility issues. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring effective treatment options are essential steps towards managing this condition and improving your quality of life. Dive into our comprehensive guide to learn more about bunions and how to keep your feet happy and healthy.
Table of Contents
Understanding Bunions (Hallux Valgus)
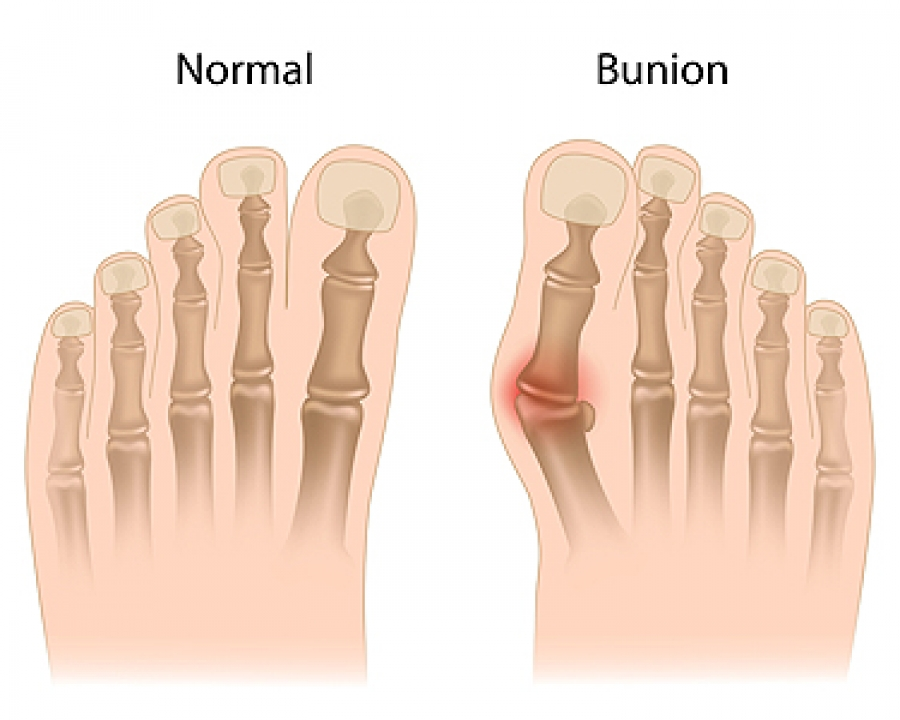
Bunions, known medically as Hallux Valgus, represent a prevalent foot condition marked by the emergence of a bony projection at the base of the big toe. This ailment unfolds as the big toe veers towards the second toe, causing joint misalignment and the characteristic bony outgrowth. Grasping the origins, recognizing the signs, and exploring effective treatment options are crucial for individuals grappling with bunions.
Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions manifest through various symptoms that illuminate the condition’s severity and progression. Prompt recognition of these signs is essential for early diagnosis and the initiation of effective treatment strategies.
The Bony Bump: A Defining Feature
- The most conspicuous symptom of a bunion is the pronounced bony outgrowth at the big toe’s base. This protrusion is a clear indicator of underlying joint dislocation rather than a mere surface-level concern.
- With the big toe’s gradual inclination towards the adjacent toes, the bony bump becomes increasingly prominent, signifying bunion formation.
Inflammation and Discomfort: Hidden Challenges
- Beyond the visible bump, bunions can provoke swelling, redness, and tenderness around the base of the big toe. These symptoms mirror the body’s response to the joint’s altered structure.
- Prompt attention and treatment of these inflammatory signs can enhance comfort and manage symptoms effectively.
Toe Misalignment: A Critical Indicator
- A less noticeable yet vital symptom is the big toe’s slow drift towards the smaller toes. This shift has a profound impact on the foot’s overall structure and is pivotal in addressing the root causes of bunions.
- Recognizing this deviation is fundamental in correcting the underlying issues associated with bunions.
Callus Formation: A Reaction to Friction
- The continuous pressure from the misaligned big toe against the second toe often leads to the formation of calluses. These hardened, thick areas of skin develop as a defense against ongoing friction.
- While seemingly minor, calluses signify the foot’s enduring stress, emphasizing the need for corrective action.
Joint Stiffness and Limited Movement: Indicators of Progression
- With the progression of the condition, the big toe may exhibit reduced mobility and heightened stiffness. Misalignment and structural changes in the joint curtail the range of motion, resulting in rigidity.
- Prompt measures to reduce this stiffness are crucial for maintaining joint flexibility.
Footwear Difficulties: The Practical Impediment
- A direct and tangible complication of bunions is the difficulty in finding comfortable, well-fitting footwear. The misalignment and protrusion make wearing regular shoes a painful ordeal without exacerbating discomfort.
- Promptly acknowledging and managing bunion symptoms can markedly assist in controlling the condition, enhancing life quality, and averting further issues.
Understanding the Origins and Risk Factors for Bunions
Unraveling the origins of bunions is crucial for both prevention and effective management. While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices and environmental influences are also significant contributors to the development of this foot condition.
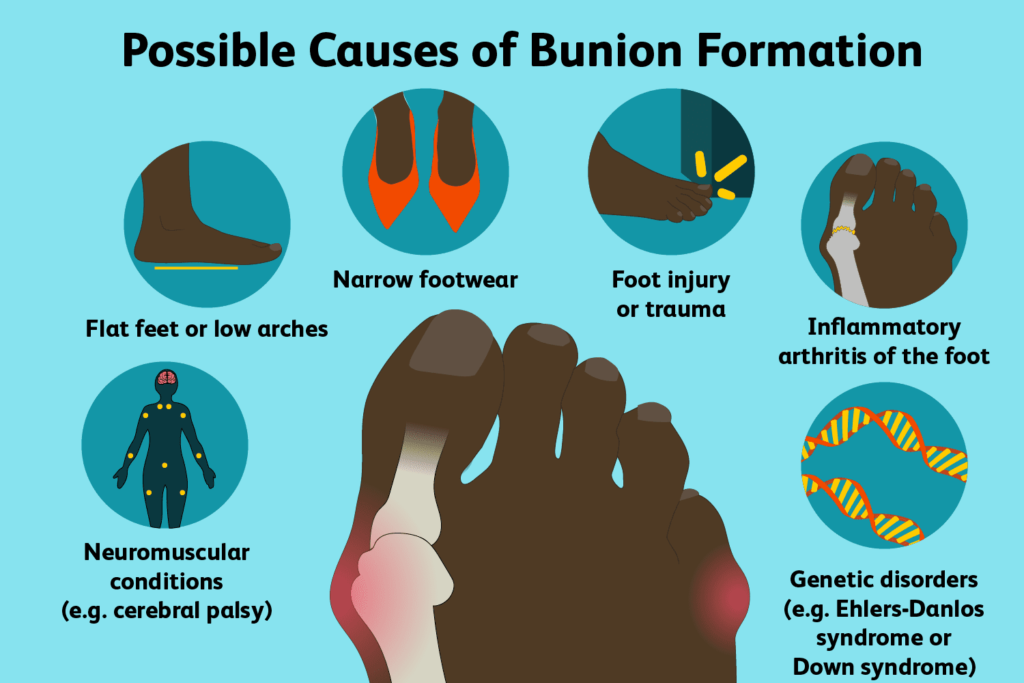
Genetic and Environmental Contributions
The emergence of bunions is frequently attributed to a blend of hereditary traits and external pressures. Inherited foot shapes may predispose individuals to bunions, yet environmental factors, such as footwear choices, can trigger or exacerbate their formation. Recognizing the interplay between these elements is essential for comprehensive care.
Inherited Overpronation
A leading cause of bunions is overpronation, characterized by an excessive inward roll of the foot while walking. This biomechanical tendency, often inherited, places individuals with a family history of such patterns at a higher risk for developing bunions.
Continuous Pressure on the Big Toe Joint
The continuous force exerted on the first metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint is a primary culprit in bunion development. Footwear that squeezes the toes or features narrow, pointed toe boxes can force the big toe inward, facilitating the formation of the distinctive bunion protrusion.
Foot Structural Anomalies
Natural variations in foot structure may predispose some individuals to bunions by affecting the distribution of pressure and weight across the foot, thereby influencing toe alignment. Addressing these structural concerns is key to mitigating the risk of bunions.
Impact of Health Conditions on Joint Health
Certain medical conditions, notably arthritis, can compromise joint health and contribute to the development of bunions. The changes in joint structure and function associated with arthritis may encourage the misalignment of the big toe, indirectly leading to bunions.
Effective Strategies for Relief and Control

Effectively dealing with bunions involves a comprehensive strategy aimed at reducing discomfort and preventing further deformation.
Selecting the Right Shoes: A Crucial Measure
Emphasizing Fit and Comfort:
Selecting footwear with a broad, roomy toe box is essential for those with bunions. Shoes that provide sufficient space for the toes can minimize pressure on the bunion, alleviating pain and potentially decelerating the condition’s progression. Ensuring shoes are comfortable and fit well is crucial for bunion sufferers.
Supportive Orthotics: Custom and Over-the-Counter Options
Customized Foot Support:
For targeted support, custom-made orthotics or off-the-shelf options can play a pivotal role in bunion management. These devices aim to correct foot pronation and promote proper alignment, facilitating even pressure distribution and shock absorption. This support can lessen bunion discomfort and hinder its progression.
Accessibility of Over-the-Counter Supports:
Readily available over-the-counter insoles provide a convenient, though less customized, support option. These inserts can be easily incorporated into daily footwear, offering enhanced foot mechanics and comfort.
Pain Relief Strategies: Easing Bunion Discomfort
Utilizing Over-the-Counter Medications:
Over-the-counter pain relievers, like NSAIDs, offer effective relief from bunion-related pain and inflammation. It’s important to adhere to dosage recommendations and consult a healthcare professional for safe usage guidelines.
Physical Therapy: Enhancing Foot Health
Focused Strengthening and Flexibility:
Engaging in physical therapy that includes specialized foot exercises can be extremely beneficial for those with bunions. Such exercises aim to increase toe flexibility, enhance joint mobility, and correct muscular imbalances, supporting a holistic approach to bunion management. Integrating physical therapy into a comprehensive treatment plan can significantly improve symptoms and overall foot health.
Atlas Arch Support Insoles: Enhancing Bunion Management
Atlas Arch Support insoles present a beneficial solution for individuals dealing with bunions, featuring unique attributes aimed at providing relief and support:
Pronation Management
Overpronation, where the foot excessively rolls inward during walking, significantly contributes to bunion formation. The design of Atlas Arch Support insoles counters this by promoting proper foot alignment. This crucial adjustment minimizes stress on the big toe joint, potentially slowing the progression of bunions.
Balanced Weight Distribution
Designed to distribute body weight uniformly across the foot, these insoles alleviate pressure on areas prone to bunions. This even distribution is particularly helpful in reducing discomfort during extended periods of standing or walking.
Improved Alignment
By supporting the arch, Atlas Arch Supports play a pivotal role in correcting foot alignment. This support lessens the strain on the big toe joint, aiding in the management of bunion-related pain and preventing further misalignment.
Shock Absorption
With their advanced cushioning, Atlas insoles absorb the shocks associated with walking or running. This feature is crucial for minimizing impact on the bunion, thereby reducing pain and improving comfort during physical activities.

Customized Fit
Available in various sizes and shapes, Atlas Arch Support insoles offer a personalized fit for different foot types, ensuring targeted support exactly where it’s needed.
Enhanced Comfort
By improving overall foot comfort and reducing pressure points, these insoles allow individuals with bunions to go about their daily activities with less discomfort, thereby improving their quality of life.
Preventative Measures
For those at risk of developing bunions, such as people with flat feet or those who overpronate, Atlas Arch Support insoles act as an effective preventative measure. By addressing the underlying causes of bunions, these insoles can help prevent or delay their onset.
Overall, Atlas Arch Support insoles are highly recommended for their comprehensive approach to supporting foot health, offering significant benefits for those looking to manage or prevent bunions through improved support and alignment.
FAQ Section
Q1: What exactly is a bunion?
A1: A bunion, or Hallux Valgus, is a bony protrusion at the base of the big toe, caused by the misalignment of the toe’s joints. This condition often leads to discomfort and pain due to the bump and associated symptoms.
Q2: What causes bunions?
A2: Bunions can result from genetic predispositions, environmental factors such as wearing tight, narrow shoes, and conditions like arthritis. Overpronation and continuous pressure on the big toe joint are also significant contributors.
Q3: How can I alleviate bunion pain?
A3: Pain relief strategies include selecting the right shoes with a broad toe box, using supportive orthotics, and engaging in physical therapy exercises to improve flexibility and joint mobility. Over-the-counter medications may also help manage pain and inflammation.
Q4: Are there preventative measures for bunions?
A4: Yes, wearing properly fitting footwear, using arch support insoles, and addressing any biomechanical issues like overpronation can help prevent the development or worsening of bunions.
Q5: Can bunions be treated without surgery?
A5: Many non-surgical options, such as orthotic support, proper footwear, and physical therapy, can effectively manage bunion symptoms. However, severe cases may require surgical intervention for relief.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing bunions (Hallux Valgus) is crucial for maintaining foot health and overall well-being. By recognizing the signs early, adopting preventative measures, and exploring treatment options, individuals can significantly reduce discomfort and improve their quality of life. Remember, taking proactive steps towards foot care can lead to happier, healthier feet.
MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers