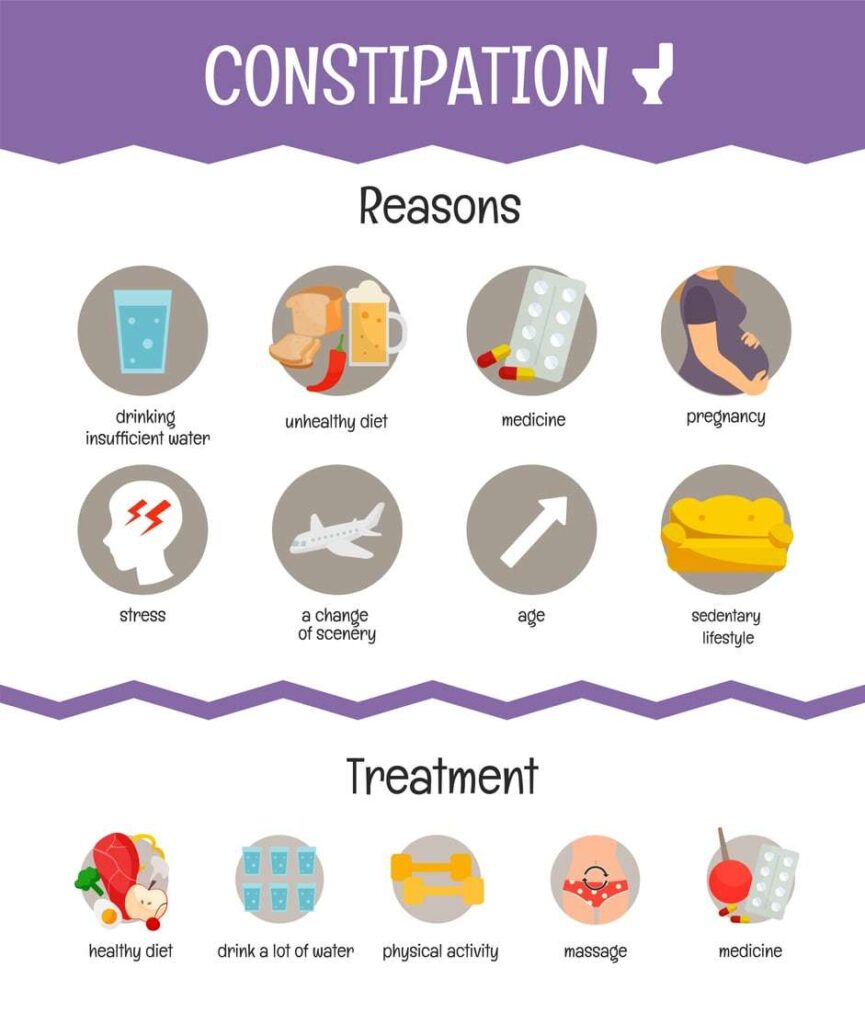
Constipation is a common digestive issue that affects people of all ages, causing discomfort and hindering daily activities. While it may be a temporary inconvenience for some, for others, it’s a chronic condition requiring careful management. This article explores the causes of constipation and offers effective solutions for relief, aiming to restore your digestive health and improve your quality of life.
Table of Contents
Introduction
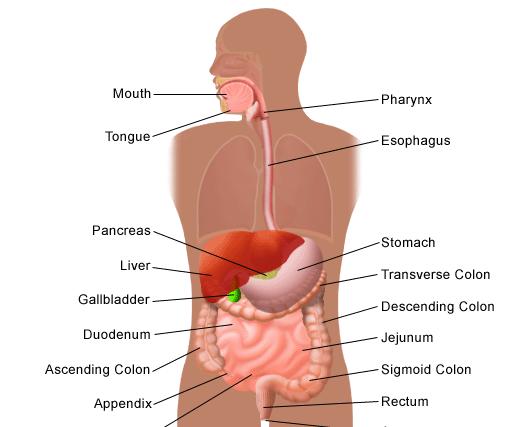
Understanding the basics of constipation and recognizing its impact on health is the first step toward relief. Constipation is characterized by fewer than three bowel movements per week, often accompanied by hard, dry stools that are difficult to pass. Addressing this issue is crucial, not only for comfort but also for preventing more serious health complications.
Causes of Constipation
- Dietary Factors:
- Low Fiber Intake: Fiber adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to pass. A diet low in fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can lead to constipation.
- High Dairy or Meat Consumption: Consuming large amounts of dairy products or red meats, which are low in fiber, can contribute to constipation.
- Processed and Fast Foods: These foods often lack fiber and can be high in fats and sugars, slowing down digestion.
- Hydration Levels:
- Insufficient Fluid Intake: Not drinking enough water can lead to harder, drier stools that are difficult to pass. Dehydration is a common cause of constipation.
- Excessive Alcohol or Caffeine: These can lead to dehydration, worsening constipation.
- Physical Activity:
- Lack of Exercise: Regular physical activity helps stimulate intestinal functions. A sedentary lifestyle can slow down digestion and bowel movements.
- Medications and Supplements:
- Certain Medications: Some medications, including painkillers (especially narcotics), some antacids, antidepressants, and iron supplements, can cause constipation as a side effect.
- Overuse of Laxatives: Regular use of laxatives can weaken the bowel’s natural ability to contract, leading to dependency and worsening constipation over time.
- Health Conditions:
- Digestive System Disorders: Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and intestinal obstructions can cause constipation.
- Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders: Hypothyroidism, diabetes, and electrolyte imbalances (such as high calcium levels) can affect bowel movements.
- Neurological Conditions: Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and multiple sclerosis can affect the nerves that help control bowel movements.
- Psychological Factors:
- Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can lead to changes in bowel habits, including constipation.
- Depression: This can affect appetite and activity levels, leading to constipation.
- Lifestyle Choices:
- Ignoring the Urge to Go: Regularly ignoring the urge to have a bowel movement can lead to constipation.
- Routine Changes: Travel or changes in daily routine can disrupt normal bowel function.
- Age and Life Stages:
- Aging: The digestive system slows down with age, and older adults are more likely to take medications that can cause constipation.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure on the intestines from the growing uterus can lead to constipation in pregnant women.
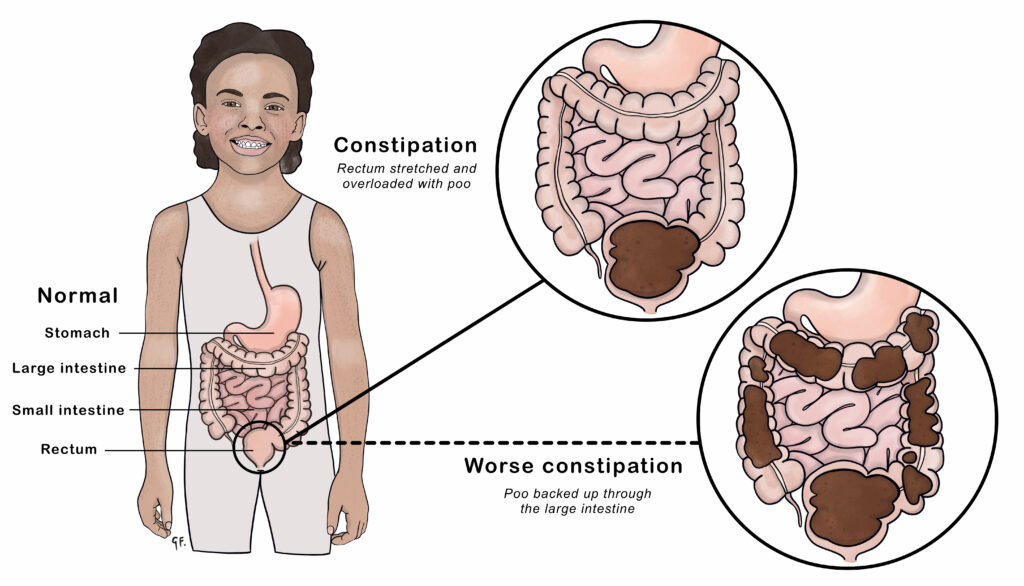
Effective Solutions for Constipation Relief
1. Increase Fiber Intake
- Dietary Fiber: Consuming foods high in fiber such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds can help increase stool bulk and ease its passage.
- Fiber Supplements: If dietary changes are insufficient, over-the-counter fiber supplements like psyllium husk can be helpful.
2. Stay Hydrated
- Water: Drinking plenty of water daily is crucial. Water softens the stool, making it easier to pass.
- Limit Dehydrating Beverages: Reducing intake of caffeine and alcohol, which can contribute to dehydration, is also advised.
3. Regular Physical Activity
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can stimulate digestion and help relieve constipation.
- Movement: Even simple movements or light stretching can be beneficial, especially for those with limited mobility.
4. Mind Your Medications
- Review Medications: Some medications can cause constipation. Consult with a healthcare provider to see if alternatives are available.
- Use Laxatives Wisely: While over-the-counter laxatives can provide short-term relief, they should not be relied upon for long-term use without a doctor’s guidance.
5. Establish a Routine
- Regular Bathroom Habits: Try to go to the bathroom at the same time each day, especially after meals, to take advantage of the body’s natural rhythms.
- Don’t Ignore the Urge: Delaying bowel movements can lead to harder stools and worsen constipation.
6. Probiotics
- Fermented Foods: Consuming probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi can improve gut health and regularity.
- Supplements: Probiotic supplements may also be beneficial, especially for those with digestive issues like IBS.
7. Manage Stress
- Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress, which may in turn help relieve constipation.
8. Consider Herbal Remedies
- Herbal Teas: Certain herbal teas, such as senna, peppermint, and ginger, are known for their mild laxative effects and can promote bowel movements.
9. Consult Healthcare Professionals
- Seek Advice: If constipation persists or is accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain, blood in the stool, or unexpected weight loss, it’s important to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can offer tailored advice and treatment options, including prescription medications if necessary.
10. Evaluate Your Diet
- Limit Low-Fiber Foods: Reduce the intake of foods low in fiber, such as meat, dairy products, and highly processed foods, which can exacerbate constipation.
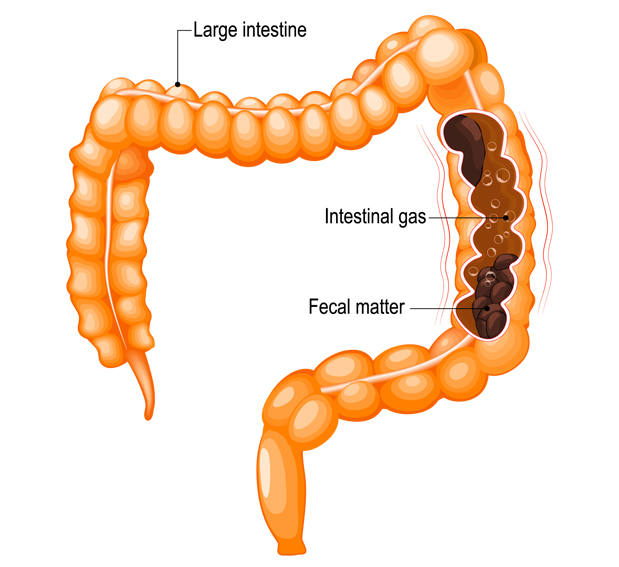
Lifestyle Modifications
1. Establish a Regular Bathroom Routine
Creating a consistent schedule for bowel movements can help regulate your digestive system. Try to use the bathroom at the same times every day, particularly after meals, to take advantage of the natural reflexes that stimulate bowel activity.
2. Increase Physical Activity
Regular exercise is crucial for stimulating intestinal activity and preventing constipation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities can include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or any other form of exercise that you enjoy and can maintain consistently.
3. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for softening stool and promoting smooth bowel movements. Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily, and consider increasing your intake if you’re active or live in a hot climate.
4. Mindful Eating
Focus on incorporating high-fiber foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. Fiber helps to increase the bulk of your stool and facilitates its passage through the intestines. Also, take your time to eat slowly and chew your food thoroughly, which can aid in digestion.
5. Limit Intake of Constipating Foods
Some foods can exacerbate constipation, including those high in fat and low in fiber, such as cheese, chips, and processed meats. Limiting your intake of these foods can help alleviate and prevent constipation.
6. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively impact your digestive system, leading to issues like constipation. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or any activity that helps you relax and unwind.
7. Adopt Healthy Sleep Habits
Getting enough sleep is vital for overall health and can also affect digestive health. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve sleep quality.
8. Listen to Your Body
Do not ignore the urge to have a bowel movement. Holding in stool can lead to constipation and other digestive issues. Responding to your body’s signals can help maintain regular bowel movements.
9. Evaluate Your Medications
Some medications, including certain painkillers, antidepressants, and iron supplements, can cause constipation as a side effect. If you suspect your medication is affecting your bowel movements, consult with your healthcare provider about possible alternatives.
10. Limit Alcohol and Caffeine
While moderate consumption may not significantly affect everyone, alcohol and caffeine can lead to dehydration, worsening constipation. Monitor your intake and ensure you’re compensating with plenty of water.
When to Seek Medical Advice
1. Persistent Symptoms
If constipation lasts longer than three weeks despite trying home remedies and lifestyle modifications, it’s time to see a doctor. Persistent constipation could be a sign of an underlying health issue that needs medical attention.
2. Blood in Stool
Seeing blood in your stool, on the toilet paper, or in the toilet bowl can be alarming. While it might be caused by hemorrhoids or anal fissures associated with straining, it’s essential to rule out more serious conditions like colorectal cancer.
3. Severe Pain
Experiencing severe abdominal pain or discomfort that doesn’t go away with a bowel movement could indicate a blockage or other serious issues that require immediate medical attention.
4. Unintended Weight Loss
Losing weight without trying can be a sign of a more serious condition, especially if accompanied by constipation.
5. Changes in Bowel Habits
Sudden changes in your bowel habits, such as consistently experiencing harder or narrower stools than usual, should prompt a visit to the doctor.
6. Use of Laxatives Without Relief
If you find yourself relying on laxatives regularly to have a bowel movement, or if laxatives no longer seem to provide relief, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
7. Accompanying Symptoms
Symptoms such as vomiting, rectal pain, or bloating, especially when combined with constipation, can indicate a more serious issue and should be evaluated by a doctor.
8. Existing Health Conditions
Individuals with certain health conditions, such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, or neurological diseases like Parkinson’s disease, might experience constipation more frequently. If you have an underlying health condition and notice changes in your bowel habits, it’s advisable to seek medical advice.
9. Impact on Daily Life
If constipation is affecting your quality of life, causing you to miss work or social activities, or significantly impacting your mental health, seek medical guidance.
10. If You’re Pregnant
Pregnant women often experience constipation due to hormonal changes and the physical pressure of the growing uterus. While it’s common, if constipation becomes severe or is accompanied by other symptoms like abdominal pain, consulting a healthcare provider is crucial.

Conclusion
Managing constipation effectively requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on diet, hydration, exercise, and lifestyle. By understanding the causes and implementing the solutions outlined in this article, you can achieve relief and improve your digestive health.
FAQs
- How much fiber should I aim for daily to prevent constipation? Aim for 25 to 30 grams of fiber per day, along with sufficient fluid intake.
- Can too much fiber worsen constipation? Yes, without adequate water, high fiber intake can cause bloating and make constipation worse.
- How long should I try home remedies before seeing a doctor? If there’s no improvement after a week of consistent home management, consult a healthcare provider.
- Can constipation be a sign of a more serious condition? In some cases, yes. Persistent constipation warrants medical evaluation to rule out underlying conditions.
- Are there any exercises specifically beneficial for constipation? Activities that engage the core, like yoga or Pilates, can be particularly beneficial.


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers