Discover essential foot care strategies for seniors to prevent common age-related issues. Learn effective tips and practices to maintain foot health and mobility in elderly individuals
Introduction
Foot care is a crucial aspect of health, especially for the elderly, as it significantly impacts their mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. Age brings with it a range of foot-related issues, from dry skin and brittle nails to more severe conditions like arthritis, diabetes-related complications, and circulatory problems. This comprehensive guide aims to explore the importance of foot care for the elderly, highlighting preventive measures for common age-related foot problems and offering practical advice for maintaining foot health.
Table of Contents

Understanding the Importance of Foot Care in the Elderly
As individuals age, the feet often show the first signs of health issues due to decades of wear and tear, decreased circulation, and changes in the structure of the feet and skin. Proper foot care becomes increasingly important to prevent discomfort, injuries, and complications that can lead to reduced mobility and independence.
Common Age-Related Foot Problems
The aging process can significantly impact foot health, leading to a variety of common age-related foot problems. These issues, if not properly managed, can impair mobility and quality of life. Understanding these conditions is the first step towards prevention and effective management. Here’s a closer look at each problem and its implications:
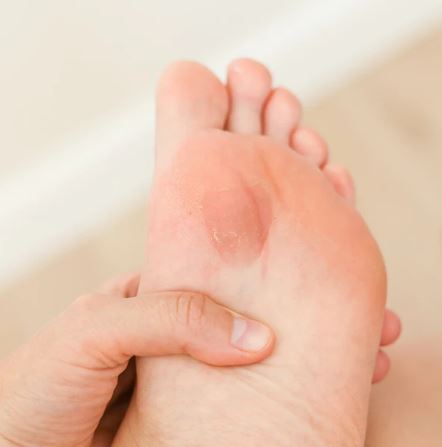
1. Dry Skin and Calluses
Cause: As we age, the skin on our feet becomes thinner and loses its elasticity and moisture, leading to dry, cracked skin. The lack of moisture increases the risk of callus formation, especially in areas subjected to friction or pressure.
Management: Regular moisturizing with creams designed for foot skin, gentle use of pumice stones to manage calluses, and wearing well-fitted shoes can help manage dry skin and prevent callus formation.
2. Brittle Nails
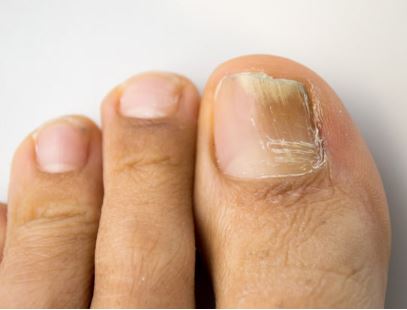
Causes: Age can cause changes in nail texture, leading to thickened, brittle nails. These changes make nails more susceptible to fungal infections, which thrive in warm, moist environments like shoes.
Management: Keeping nails trimmed straight across and avoiding tight shoes can prevent complications. If a fungal infection is suspected, consulting a healthcare provider for appropriate antifungal treatments is crucial.
3. Arthritis

Causes: The foot and ankle contain more than 30 joints, making them vulnerable to arthritis. Osteoarthritis results from wear and tear over the years, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition that can cause joint pain and deformity.
Management: Managing arthritis involves a combination of medication to reduce inflammation, orthotics to support the joints, and exercises to maintain mobility. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct deformities or fuse joints to reduce pain.
4. Diabetes-Related Complications
Neuropathy and Peripheral Arterial Disease: Diabetes can damage nerves (neuropathy), leading to loss of sensation in the feet. This makes it difficult to detect injuries, which, coupled with poor circulation (peripheral arterial disease), can lead to slow-healing wounds and infections.
Management: Diabetes management, including blood sugar control, regular foot inspections, and wearing diabetic-friendly shoes, can help prevent serious complications. Any wounds or changes in foot appearance should prompt immediate medical consultation.
5. Circulatory Problems
Causes: Reduced blood flow, often associated with aging and conditions like peripheral arterial disease, can cause swelling, numbness, and delayed wound healing. These circulatory issues increase the risk of infections and ulcers.
Management: Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight can improve circulation. The Elevating the feet when sitting and wearing compression stockings may also help reduce swelling.
Awareness and proactive management of these common age-related foot problems can significantly enhance comfort, mobility, and overall quality of life for the elderly. Regular foot care, including daily inspections and proper hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and seeking timely medical advice, are key strategies in preventing and managing these conditions. Collaboration with healthcare providers, especially podiatrists, can offer tailored advice and treatment options to address individual needs and challenges associated with aging feet.
Preventive Measures for Age-Related Foot Problems
1. Regular Inspections
Self-Examinations: Encourage daily foot checks to identify any changes or issues, such as cuts, sores, swelling, or nail problems.
Professional Assessments: Regular visits to a podiatrist for professional inspections can catch problems early and prevent complications.
2. Skin and Nail Care
Moisturizing: Daily application of moisturizer can prevent dry skin and cracks.
Proper Nail Trimming: Cut nails straight across and not too short to avoid ingrown toenails and infections.
3. Footwear and Orthotics
Supportive Shoes: Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide good support and distribute weight evenly.
Custom Orthotics: Consider using orthotic inserts prescribed by a podiatrist to correct biomechanical issues and reduce pressure points.
4. Exercise and Stretching
Promote Circulation: Regular, gentle exercises like walking or swimming can improve blood flow.
Flexibility: Stretching and flexibility exercises help maintain joint health and prevent stiffness.
5. Managing Underlying Health Conditions
Diabetes Care: Strict control of blood sugar levels and regular foot examinations are crucial for preventing diabetic foot complications.
Arthritis Management: Anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy can help manage arthritis symptoms in the feet.
Practical Tips for Elderly Foot Care
Keep Feet Clean and Dry: Wash feet daily with mild soap and warm water, and dry thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
Avoid Going Barefoot: Wearing shoes or slippers, even indoors, can protect feet from injuries and infections.
Use Corrective Devices if Needed: Devices like toe separators, bunion pads, or arch supports can provide relief from discomfort and prevent further deformities.
Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet: Good nutrition and hydration are essential for skin health and wound healing.
Elevate Feet: Elevating the feet when sitting can help reduce swelling.
The Role of Caregivers in Elderly Foot Care
Caregivers play a vital role in assisting with foot care, especially for those who have difficulty reaching their feet or identifying problems. They can help with daily inspections, ensure the use of proper footwear, and assist in arranging medical appointments.
Seeking Professional Help
Consult a healthcare provider or a podiatrist if any of the following occur:
– Persistent pain or swelling in the feet or ankles
– Changes in skin color or temperature
– Sores or wounds that do not heal
– Signs of infection (redness, warmth, tenderness)
– Ingrown toenails or problematic foot fungus
Conclusion
Foot care for the elderly is not just about preventing discomfort; it’s about preserving mobility, independence, and quality of life. By adopting preventive measures, being vigilant about foot health, and seeking professional advice when necessary, older adults can maintain healthy feet and continue to lead active, fulfilling lives. Regular foot care should be an integral part of overall health maintenance, ensuring that the golden years are enjoyed with comfort and freedom of movement.



MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers