Discover empowering insights into arthritis types, causes, and effective treatments. Dive into our guide for actionable tips and dietary advice to enhance your joint health and live pain-free.
Introduction
Arthritis, a term that encompasses a variety of conditions characterized by joint inflammation and pain, significantly impacts the lives of millions worldwide. Understanding the nuances of its types, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and relief. This article delves into the primary forms of arthritis, offering expert insights into their diagnosis, symptoms, and innovative care strategies. Whether you’re seeking to understand your own symptoms or looking for ways to support a loved one, our comprehensive guide provides the knowledge and tools you need for a healthier, more comfortable life.
Table of Contents
Arthritis Types: Causes and Symptoms
Arthritis encompasses a range of conditions marked by joint inflammation and pain. Each type has unique causes and symptoms, requiring specific diagnostic and management strategies. Here’s a detailed overview of the primary forms of arthritis, focusing on their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
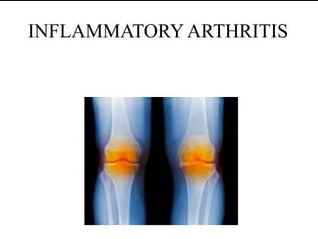
Inflammatory Arthritis
Causes
This type results from an autoimmune reaction where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues, causing joint and sometimes organ inflammation. Genetic predispositions and environmental factors can trigger these autoimmune responses.
Symptoms
Symptoms include continuous joint pain, stiffness (notably in the morning or after inactive periods), swelling, and redness. Systemic symptoms might include fatigue, fever, and appetite loss. Without proper treatment, chronic inflammation can cause joint damage and deformity.
Treatment Options
Medications:
- Medications: DMARDs (e.g., methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide) slow disease progression. Biologic response modifiers (e.g., TNF inhibitors like etanercept and adalimumab, IL-6 inhibitors like tocilizumab) target specific immune pathways. NSAIDs and corticosteroids help manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Custom exercises improve joint flexibility and muscle strength.
Surgery: Options like synovectomy, joint replacement, or fusion may be necessary for severe cases.
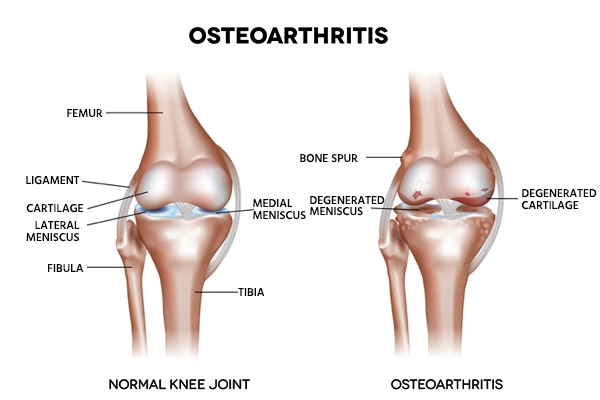
Osteoarthritis
Causes
The most common arthritis form, osteoarthritis, stems from cartilage breakdown in joints, with age, injury, obesity, and genetics as major risk factors. This wear and tear can lead to direct bone-on-bone friction, causing pain and movement restrictions.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, reduced flexibility, a grating sensation during movement, and bone spurs. It often affects hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Treatment Options
Medications: Acetaminophen for pain, NSAIDs for pain and inflammation, and corticosteroid injections for inflammation.
Physical Therapy: Strengthens muscles around joints and improves flexibility.
Weight Management: Reduces stress on weight-bearing joints.
Assistive Devices: Canes or braces aid joint function.
Surgery: Joint replacement for severe damage.
Connective Tissue Disease (CTD)
Causes
These disorders affect the body’s structural proteins due to an autoimmune attack on tissues, with genetics playing a role in susceptibility. The exact triggers are often unknown.
Symptoms
Joint pain and inflammation are common, with specific symptoms like skin rashes or dry eyes depending on the condition. CTDs can also impact internal organs.
Treatment Options
Medications: NSAIDs, corticosteroids, DMARDs, biologics, and antimalarials like hydroxychloroquine for lupus.
Physical Therapy: Maintains mobility.
Specialist Consultations: A multidisciplinary approach may be required.
Infectious Arthritis
Causes
Bacteria, viruses, or fungi can infect joints through the bloodstream or direct injury, leading to this condition.
Symptoms
It typically presents with severe joint pain, swelling, redness, warmth, and sometimes fever and chills, usually affecting one joint.
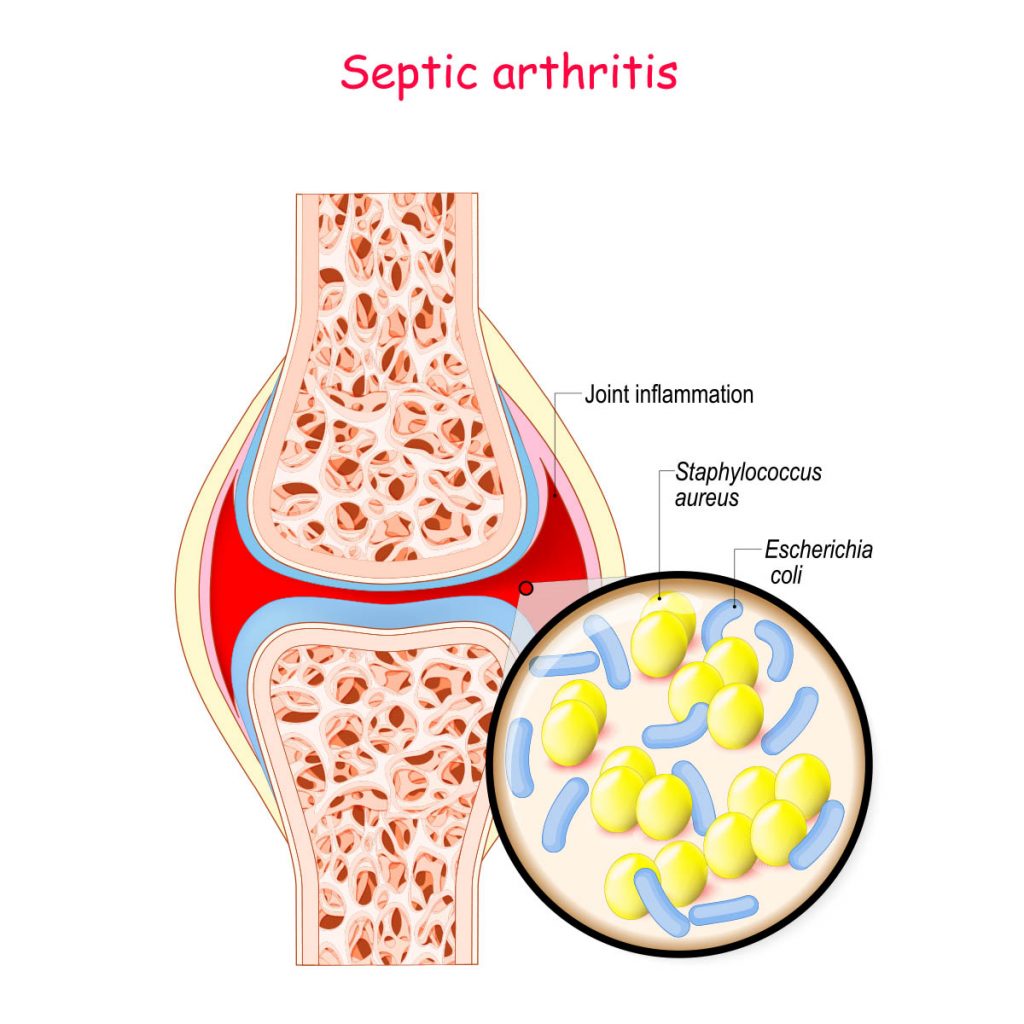
Treatment Options
Antimicrobials: Immediate use of antibiotics or antifungals based on the infection type.
Joint Drainage: To remove infected fluid and relieve symptoms.
Metabolic Arthritis (Gout)
Causes
High blood levels of uric acid lead to crystal deposition in joints, with diet, obesity, certain medications, and kidney issues as contributing factors.
Symptoms
Gout causes sudden, severe joint pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness, often in the big toe, with attacks typically occurring at night.
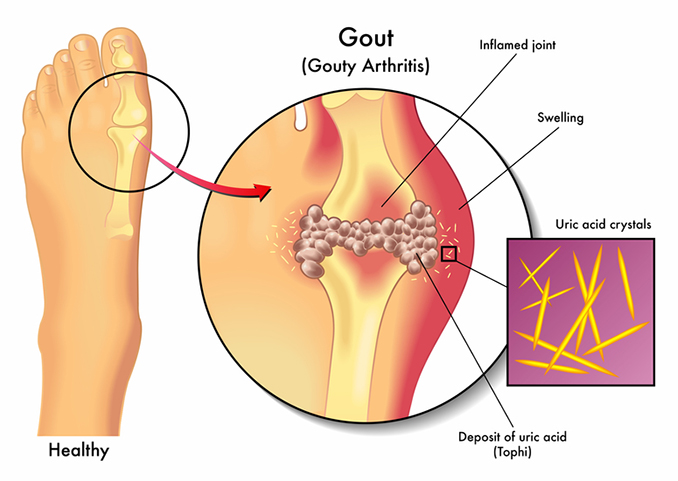
Treatment Options
Medications: NSAIDs for acute attacks, colchicine for pain, corticosteroids for those unable to take other medications, and urate-lowering therapy to prevent future attacks.
Lifestyle Changes: Dietary adjustments, weight loss, and reduced alcohol intake.
Physical Therapy: Helps maintain joint function and manage pain.
Dietary Approaches and Supplement Use
The Role of Nutrition in Arthritis Management
Nutrition significantly influences it’s symptoms, with certain diets either mitigating or exacerbating inflammation, a central component of arthritis-related discomfort and disease progression. A well-balanced dietary regimen can aid in controlling inflammation, bolstering joint function, and promoting overall health.
Incorporating Anti-inflammatory Foods
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory items can markedly diminish it’s symptoms. Key foods include:
- Omega-3-rich Fatty Fish: Varieties like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are known for their inflammation-reducing effects.
- Antioxidant-packed Leafy Greens: Such as spinach, kale, and collard greens, which are loaded with vitamins that fight inflammation.
- Nutrient-dense Nuts and Seeds: Including almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds, which provide healthy fats and support joint health.
- Antioxidant-rich Berries and Fruits: Strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges help curb inflammation.
These dietary choices help lower bodily inflammation, potentially easing pain and enhancing joint mobility.
Foods to Avoid
Some foods can trigger inflammation and aggravate it’s symptoms, such as:
- Processed and High-Sugar Foods: These can elevate inflammation and contribute to weight gain.
- Saturated and Trans Fats: Found in red meats and processed items, these fats should be consumed in moderation.
Minimizing intake of these foods can aid in controlling it’s symptoms and fostering better health.
Supplemental Support for Arthritis
Certain supplements may offer added benefits for it’s management:
- Fish Oil: A source of omega-3 fatty acids, it can help lessen joint inflammation.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: Commonly combined to aid in pain relief and enhance joint function.
- Curcumin: Derived from turmeric, it’s celebrated for its strong anti-inflammatory effects.
Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential to determine suitable dosages and ensure the safety of these supplements.
Adhering to a Healthy Eating Plan
A diet emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods, such as the Mediterranean diet, is beneficial for individuals with arthritis. This diet includes:
- A diverse array of fruits and vegetables, offering antioxidants and nutrients.
- Whole grains, providing essential fiber and nutrients.
- Healthy fats, like those from olive oil and nuts, known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Incorporating these elements into daily meals can support joint health and overall well-being.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Prior to implementing significant dietary changes or beginning new supplements, consulting with healthcare experts is crucial. They can offer tailored advice that considers your specific health conditions, medications, and needs, ensuring your dietary and supplement choices safely complement your arthritis management strategy.
By integrating these nutritional strategies and supplement options into your care regimen, alongside conventional medical treatments and physical therapy, you can effectively manage it, reduce discomfort, improve mobility, and enhance your quality of life.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are the main types of arthritis?
A1: Arthritis includes several types, such as inflammatory, osteoarthritis, connective tissue disease, infectious, and metabolic arthritis (gout), each with unique causes and symptoms.
Q2: How can diet influence arthritis symptoms?
A2: Nutrition plays a significant role in managing arthritis. Anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3-rich fish, leafy greens, nuts, and berries can reduce symptoms, while processed and high-sugar foods may exacerbate them.
Q3: Are there effective treatments for arthritis?
A3: Yes, treatment options vary by type but may include medications like DMARDs and NSAIDs, physical therapy, weight management, and in severe cases, surgery. Supplements such as fish oil, glucosamine, and curcumin can also support joint health.
Q4: Can lifestyle changes impact arthritis?
A4: Absolutely. Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle changes such as adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve quality of life for those with arthritis.
Conclusion
Arthritis, while challenging, is not insurmountable. With a deeper understanding of its types and causes, along with a proactive approach to treatment and lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. Embracing a holistic approach that combines medical treatments with nutritional and lifestyle strategies is key to reducing discomfort, improving mobility, and enhancing overall well-being. Remember, consulting healthcare providers before making significant changes is essential to ensure your management plan is safe and effective. Together, we can unlock the path to better joint health and comfort.


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Pea Proteins: The Best Plant-Based Protein Alternative?
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Moringa Powder / Moringa Supplement
Green Superfood: The Ultimate Guide to Moringa Leaf Powder
Moringa Powder
Supercharge Your Diet: The Incredible Impact of Moringa Leaf Powder
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Shin Splints / Foot Health / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Overcoming Shin Splints – Discover Healing Strategies