Help Digestive System:
Let’s discuss more…………….
The digestive system plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being. It is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients, absorbing those nutrients, and eliminating waste products. A healthy digestive system ensures proper nutrient absorption, supports immune function and contributes to overall vitality. Therefore, it is crucial to adopt habits that promote digestive health.
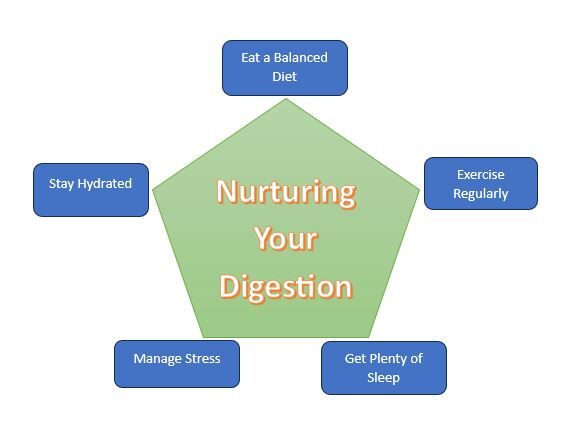
Here are the 5 effective ways to take care of your digestive system:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet:
Eating a balanced diet is fundamental to maintaining a healthy digestive system. The food you consume directly impacts the functioning of your digestive tract, influencing everything from nutrient absorption to bowel regularity.
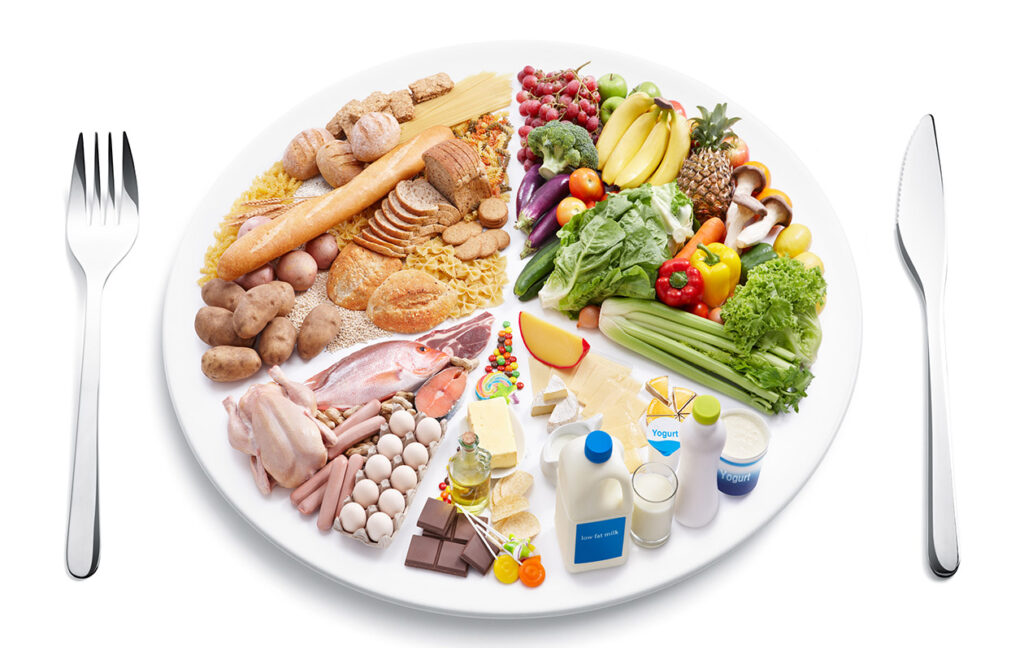

Here’s how you can optimize your diet for digestive health:
- Fiber-Rich Foods:
- Include plenty of fiber in your diet, as it promotes regular bowel movements and prevents constipation.
- Whole grains like oats, barley, and brown rice, as well as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts, are excellent sources of fiber.
- Probiotic Foods:
- Incorporate probiotic-rich foods into your diet to support a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
- Yogurt, kefir, kombucha, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso are all examples of probiotic foods that can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome.
- Lean Proteins:
- Choose lean sources of protein such as poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils.
- These protein sources are easier to digest compared to fatty meats, which can slow down digestion and lead to discomfort.
- Healthy Fats:
- Include healthy fats in your diet, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
- These fats support the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and help keep the digestive system lubricated.
- Limit Processed Foods:
- Minimize your intake of processed and refined foods, as they often lack fiber and essential nutrients.
- These foods can also contain additives and preservatives that may disrupt digestive function.
- Drink plenty of water:
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your digestive system hydrated and functioning optimally.
- Water helps soften stool, making it easier to pass, and aids in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- Moderate Portion Sizes:
- Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent overeating, which can overwhelm the digestive system and lead to discomfort.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can also help maintain steady energy levels and support digestion.
- Mindful Eating:
- Practice mindful eating by paying attention to the sensory experience of eating and listening to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Chew your food thoroughly and eat slowly to aid digestion and prevent overeating.
- Limit Trigger Foods:
- Identify any foods that trigger digestive discomfort or symptoms and limit or avoid them as needed.
- Common trigger foods include spicy foods, fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners.
- Seek Professional Advice:
- If you have specific dietary concerns or digestive issues, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional.
- They can provide personalized recommendations tailored to your individual needs and help you optimize your diet for digestive health.
2. Stay Hydrated:
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Water plays a crucial role in various digestive processes, including the breakdown of food, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of waste. In general calculation, a man needs about 15.5 cups (3.7 liters) of fluids per day and a woman needs about 11.5 cups (2.7 liters) of fluids per day.
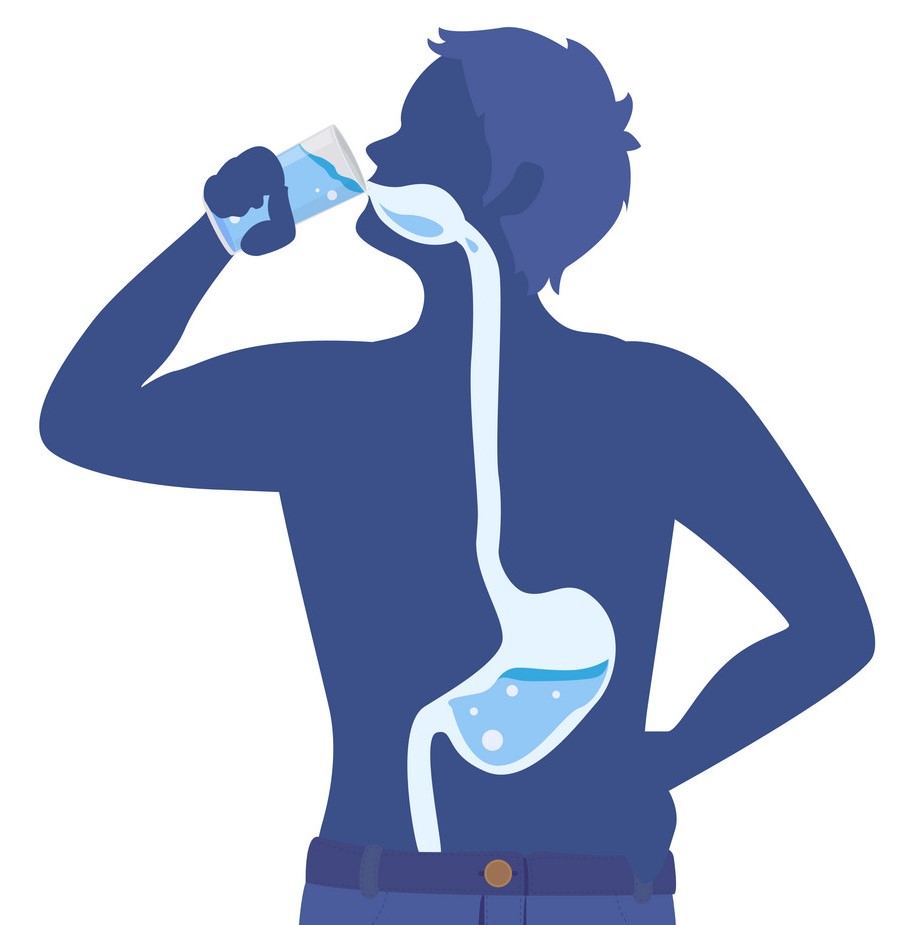

Here’s why hydration is important for digestive health and how you can ensure you’re getting enough fluids:
- Optimal Digestion:
- Water helps break down food in the stomach and intestines, facilitating the digestion process.
- It softens food particles, making them easier to swallow and digest.
- Without adequate hydration, digestion can slow down, leading to constipation and discomfort.
- Nutrient Absorption:
- Water is necessary for the absorption of nutrients from the food you eat.
- It helps transport nutrients through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream, where they can be used by the body for various functions.
- Proper hydration ensures efficient nutrient absorption and supports overall health.
- Prevention of Constipation:
- Dehydration can contribute to constipation by causing dry and hard stools that are difficult to pass.
- Drinking enough water softens stool and adds bulk to the stool, making it easier to move through the digestive tract.
- This helps prevent constipation and promotes regular bowel movements.
- Maintenance of Gut Health:
- Adequate hydration supports a healthy balance of beneficial bacteria in the gut microbiome.
- These bacteria play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function.
- Drinking enough water helps maintain optimal conditions for the growth and activity of these beneficial bacteria.
- Prevention of Digestive Issues:
- Dehydration can exacerbate digestive issues such as acid reflux, indigestion, and bloating.
- By staying hydrated, you can help prevent these discomforts and support overall digestive comfort.
Now that you understand the importance of staying hydrated for digestive health, here are some tips to ensure you’re getting enough fluids:

- Drink Water Regularly:
- Aim to drink water throughout the day, rather than waiting until you feel thirsty.
- Keep a reusable water bottle with you and sip on it regularly to stay hydrated.
- Monitor Urine Color:
- Pay attention to the color of your urine as it can indicate your hydration status.
- Ideally, urine should be pale yellow to clear.
- Dark yellow urine may indicate dehydration, so drink more water if your urine is darker in color.
- Incorporate Hydrating Foods:
- Many fruits and vegetables have high water content and can contribute to your overall hydration.
- Include hydrating foods such as watermelon, cucumber, oranges, strawberries, and lettuce in your diet.
- Limit Dehydrating Beverages:
- Minimize your intake of caffeinated and alcoholic beverages, as they can have a diuretic effect and increase fluid loss.
- If you consume these beverages, be sure to drink extra water to offset their dehydrating effects.
- Adjust Fluid Intake for Activity Level:
- Increase your fluid intake if you’re physically active or in hot weather to replace fluids lost through sweat.
- Drink water before, during, and after exercise to stay properly hydrated.
- Listen to Your Body:
- Pay attention to your body’s thirst signals and drink water whenever you feel thirsty.
- Thirst is a sign that your body needs fluids, so be sure to respond to it promptly.
3. Exercise Regularly:
Exercise is not only beneficial for cardiovascular health and weight management but also plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Regular physical activity can help improve digestion and alleviate symptoms such as bloating, constipation, and indigestion. An adult should exercise at least an average of 60 minutes per day of moderate-to-vigorous intensity.
Here are several ways exercise supports digestive health:
- Promotes Regular Bowel Movements:
- Exercise stimulates the muscles of the digestive tract, helping to move food through the intestines more efficiently.
- This can prevent constipation and promote regularity by encouraging bowel movements.
- Reduces Bloating:
- Physical activity can help reduce bloating by facilitating the passage of gas through the digestive tract.
- Aerobic exercises, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, increase blood flow to the abdominal organs, which can aid in digestion and reduce bloating.
- Supports Gut Motility:
- Gut motility refers to the coordinated contractions of the muscles in the digestive tract that propel food forward.
- Regular exercise can help regulate gut motility, preventing issues such as slow digestion or gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Boosts Metabolism:
- Exercise helps increase metabolic rate, which can improve the efficiency of digestion and nutrient absorption.
- A faster metabolism may also prevent the buildup of undigested food in the intestines, reducing the risk of digestive problems.
- Stress-Relief Strategy:
- Stress can have a significant impact on digestive health, leading to symptoms such as indigestion, stomach cramps, and diarrhea.
- Exercise is an effective stress-relief strategy, as it triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters that can help alleviate stress and anxiety.
- Maintains Healthy Weight:
- Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for digestive health, as obesity is a risk factor for conditions such as acid reflux, gallstones, and fatty liver disease.
- Regular exercise can help manage weight by burning calories and promoting fat loss.
- Improves Gut Microbiota:
- Research suggests that exercise can positively influence the composition of gut microbiota, the trillions of bacteria that inhabit the digestive tract.
- A diverse and balanced gut microbiome is associated with better digestion, immune function, and overall health.
- Enhances Circulation:
- Exercise improves blood circulation throughout the body, including to the digestive organs.
- Better circulation ensures that nutrients are delivered efficiently to the intestines for absorption and helps remove waste products from the body.
4. Manage Stress:
Managing stress is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. The gut-brain connection is well-documented, and stress can significantly impact digestive function, leading to symptoms such as indigestion, bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits. Therefore, adopting effective stress management techniques is crucial for promoting digestive health.
Here are several strategies to help you manage stress and support your digestive system:
- Practice Relaxation Techniques:
- Incorporate relaxation techniques into your daily routine to help calm your mind and body.
- Deep breathing exercises, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery are effective techniques that can reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Engage in Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise is a powerful stress-relief strategy that can benefit both your physical and mental health.
- Physical activity helps release endorphins, the body’s natural mood boosters, which can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Prioritize Sleep:
- Quality sleep is essential for stress management and overall health.
- Make sleep a priority by establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring your sleep environment is conducive to restful sleep.
- Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to feel refreshed and rejuvenated.
- Practice Mindfulness:
- Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment and can be a powerful tool for managing stress.
- Mindfulness meditation, yoga, and tai chi are practices that can help cultivate mindfulness and promote relaxation.
- Set Boundaries:
- Learn to say no to activities or commitments that add unnecessary stress to your life.
- Setting boundaries and prioritizing your own needs can help reduce overwhelm and prevent burnout.
- Take Breaks:
- Incorporate regular breaks into your day to rest and recharge.
- Whether it’s a short walk outside, a few minutes of deep breathing, or simply stepping away from your desk, taking breaks can help reduce stress and improve productivity.
- Connect with Others:
- Social support is essential for managing stress and maintaining emotional well-being.
- Spend time with friends and loved ones, and seek out supportive relationships that provide comfort and encouragement during challenging times.
- Practice Self-Care:
- Engage in activities that nourish your body, mind, and soul.
- Whether it’s taking a warm bath, reading a book, listening to music, or spending time in nature, prioritize activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
- Seek Professional Help:
- If you’re struggling to manage stress on your own, don’t hesitate to seek support from a mental health professional.
- Therapy, counseling, or support groups can provide valuable tools and resources for coping with stress and improving overall well-being.
5. Get Plenty of Sleep:
Getting plenty of sleep (7-9 hours) is crucial for maintaining optimal digestive health and overall well-being. Sleep plays a significant role in various physiological processes, including digestion, metabolism, and immune function. Lack of sleep or poor-quality sleep can disrupt these processes and contribute to digestive problems such as indigestion, bloating, constipation, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

Here’s why prioritizing sleep is essential for a healthy digestive system:
- Regulates Digestive Hormones:
- Adequate sleep helps regulate the release of hormones that influence appetite and digestion, such as ghrelin and leptin.
- Ghrelin stimulates hunger, while leptin signals satiety.
- Sleep deprivation can disrupt the balance of these hormones, leading to increased appetite and alterations in food intake, which may negatively impact digestion and weight management.
- Supports Gut Health:
- Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance of gut microbiota, the trillions of bacteria that inhabit the digestive tract.
- Disruptions in sleep patterns can alter the composition of gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis (imbalance), inflammation, and gastrointestinal problems.
- Prioritizing quality sleep can help support a diverse and healthy gut microbiome, which is essential for optimal digestion and overall health.
- Promotes Digestive Function:
- During sleep, the body focuses on repair, regeneration, and detoxification processes, including those related to digestion.
- Adequate sleep allows the digestive system to function optimally, facilitating the breakdown and absorption of nutrients from food and the elimination of waste products.
- Consistent sleep patterns help maintain regular bowel movements and prevent digestive issues such as constipation or diarrhea.
- Reduces Stress and Inflammation:
- Quality sleep is essential for reducing stress levels and lowering inflammation throughout the body, including the digestive tract.
- Chronic stress and inflammation can exacerbate digestive problems such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and peptic ulcers.
- Prioritizing sleep can help mitigate these effects and promote a healthier gut environment.
- Improves Immune Function:
- Sleep plays a critical role in supporting immune function, helping the body defend against infections and pathogens that can affect digestive health.
- Adequate sleep enhances immune response mechanisms, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal infections and inflammatory conditions that can disrupt digestion.
To prioritize sleep for better digestive health, consider the following tips:

- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s internal clock and improve sleep quality.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine:
- Develop a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
- This may include activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, practicing relaxation techniques, or listening to soothing music.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment:
- Make sure your bedroom is conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet.
- Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that support restful sleep.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed:
- Avoid electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers at least an hour before bedtime, as the blue light emitted from screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Limit Stimulants and Heavy Meals Before Bed:
- Avoid consuming caffeine, alcohol, and heavy or spicy foods close to bedtime, as they can disrupt sleep and contribute to digestive discomfort.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques:
- Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation to calm your mind and prepare for restful sleep.
Conclusion:
Taking care of your digestive system is crucial for overall health and well-being.
By adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep, you can support optimal digestive function.
Listen to your body, pay attention to digestive cues, and seek professional help if needed to ensure your digestive system stays healthy and vibrant.


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers