Explore our expert guide on shin splints, offering essential insights into causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies. Learn how to alleviate pain and prevent future occurrences with our targeted advice.
Introduction
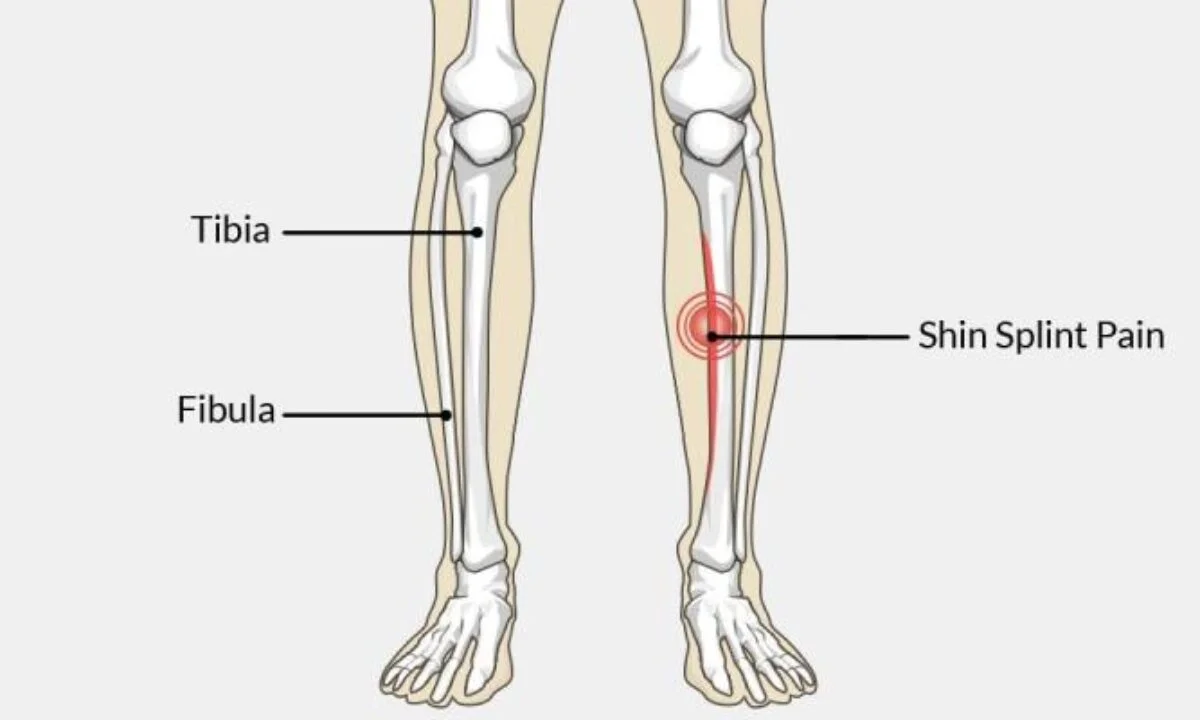
Shin splints, a common ailment among athletes and fitness enthusiasts, manifest as pain along the shinbone due to excessive stress on the lower leg tissues. This guide delves into the primary causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies to not only provide relief but also prevent future occurrences. Whether you’re a seasoned runner or a sports aficionado, understanding shin splints is crucial for maintaining your leg health and continuing your physical activities pain-free.
Table of Contents
Causes of Shin Splints
Shin splints, a frequent issue among athletes and active individuals, arise from excessive stress on the shinbone (tibia) and the tissues around it. This condition is often linked to activities that involve a lot of leg work, such as running, dancing, and various sports. Let’s delve into the primary factors that contribute to the development of shin splints:
1. Excessive Physical Activity
The main trigger for shin splints is the overuse of leg muscles, tendons, and bone tissue, common in activities requiring extensive leg movement. The repetitive stress, especially without sufficient rest, can lead to shin splints. Sudden increases in the intensity or duration of these activities can exacerbate the risk, as the body struggles to adapt quickly enough.
2. Inadequate Footwear
Footwear plays a crucial role in supporting and cushioning the feet during physical activities. Shoes that lack proper support or are not designed for specific activities can significantly contribute to the risk of developing shin splints. The absence of adequate impact absorption or correction for foot imbalances can lead to improper force distribution, straining the shinbone and surrounding tissues.
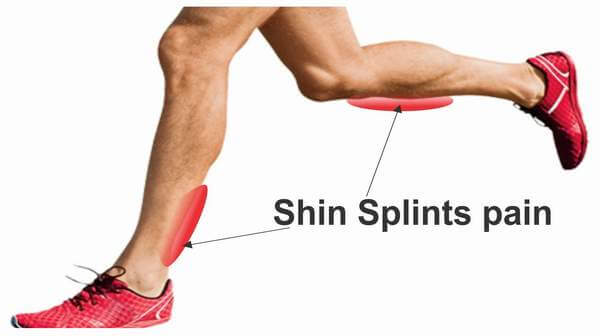
3. Biomechanical Factors
The structure of an individual’s feet and legs can greatly influence their risk of experiencing shin splints. Issues such as flat feet (overpronation) or high arches (supination) can lead to uneven stress distribution along the leg, putting additional pressure on the shinbone. Furthermore, incorrect movement techniques in activities like running or jumping can increase the risk by placing abnormal stress on the lower leg, affecting the leg’s alignment and functionality.
4. Muscle Imbalances and Flexibility Concerns
Muscular imbalances and a lack of flexibility in the lower leg are also contributing factors to shin splints. Tightness in the calf muscles, weak ankles, and limited flexibility can alter one’s gait and running patterns, thereby increasing stress on the shinbone. Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises for the lower leg muscles can mitigate these issues, improving muscle balance and flexibility.
5. Environmental and Surface Conditions
Engaging in activities on hard or irregular surfaces can escalate the risk of shin splints due to the increased impact forces exerted on the shinbone. Training in challenging environmental conditions without proper adjustment of equipment or activity intensity can further exacerbate the stress experienced by the lower legs.
Symptoms
Shin splints, a common condition among athletes and physically active individuals, are characterized by pain and discomfort along the shinbone (tibia). Understanding the symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here’s a breakdown of the key indicators:
Pain Along the Inner Edge of the Shinbone
Nature of Pain: The hallmark of shin splints is pain along the inner side of the shinbone, ranging from sharp and acute to a dull, throbbing ache. This discomfort is a clear sign of the stress and inflammation affecting the tissues that attach muscles to the bone.
Sensitivity and Tenderness
Touch Sensitivity: The shin area becomes notably tender and sensitive, with the degree of soreness varying significantly. For some, this may be a slight discomfort, while for others, it could be severe enough to disrupt daily activities.
Swelling and Inflammation
Visible Signs: Swelling along the shinbone, accompanied by inflammation, is common. Though typically mild, the swelling contributes to the discomfort experienced and indicates the severity of the condition.
Pain During Activity
Pain with Movement: Activities that involve running, jumping, or even walking can exacerbate the pain, which may initially occur only during physical exertion but can become persistent or intensify over time.
Pressure-Related Pain
Impact Sensitivity: Applying pressure to the shinbone or engaging in impact activities often worsens the pain, particularly on hard surfaces. This symptom is a key indicator of shin splints.
Additional Symptoms
Muscle Stiffness: Some individuals may notice stiffness in the lower leg muscles and a reduced range of motion, extending the discomfort beyond the immediate area of the shin splints.
Spread of Pain: In more severe cases, the pain can radiate from the shin to surrounding areas, leading to widespread discomfort in the lower leg.
Progression of Symptoms
Evolution of Discomfort: Initially, shin splint symptoms might manifest only during or after physical exertion. Without proper intervention, these symptoms can progress, leading to constant pain that affects mobility and significantly diminishes the quality of life.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing shin splints requires a detailed evaluation to accurately identify the condition and distinguish it from other potential causes of lower leg pain. This careful diagnostic process is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan. Here’s an overview of the steps involved in diagnosing shin splints:
Initial Medical History Review
Consultation: The diagnosis begins with an in-depth discussion of the patient’s medical history, focusing on any previous leg injuries, conditions affecting the lower legs, exercise routines, recent increases in physical activity, and past treatments for leg pain.
Symptom Analysis: Understanding the specifics of the symptoms, such as the onset of pain, its duration, and factors that exacerbate or alleviate it, is essential. This information helps differentiate shin splints from other similar conditions.
Physical Examination
Observation and Palpation: The doctor will visually inspect the leg for signs of swelling, redness, or deformities and palpate the shin area to locate tender spots indicative of shin splints.
Functional Tests: Patients may be asked to perform movements or exercises to evaluate biomechanics, muscle strength, and flexibility, and to identify pain triggers, such as certain walking patterns or activities.
Advanced Imaging Tests
Further testing may be necessary to rule out other conditions:
X-rays: Although shin splints do not show up on X-rays, this imaging can help exclude bone fractures that present similar symptoms.
MRI Scans: MRI scans offer a detailed view of the soft tissues surrounding the shinbone, useful for detecting bone stress reactions or distinguishing shin splints from other soft tissue injuries.
Bone Scans: For identifying stress fractures, a bone scan may be conducted, using a small amount of radioactive material to highlight areas of bone remodeling, indicative of fractures or significant stress.
Differential Diagnosis
Excluding Similar Conditions: It’s crucial to rule out other conditions with overlapping symptoms, such as compartment syndrome, stress fractures, and muscle strains. This ensures the treatment plan is specifically tailored to address shin splints, targeting the correct underlying issues.
Treatment
Managing shin splints involves a combination of immediate care strategies and long-term preventive measures. Here’s a guide to effectively addressing shin splints and safeguarding against their recurrence:
1. Rest and Recovery
Essential Downtime: Pausing high-impact activities is crucial for allowing the tissues around the shinbone to heal. The duration of rest varies with the severity of the condition but is fundamental to recovery.
Controlled Activity Resumption: Slowly reintroducing physical activities, with careful monitoring of intensity and duration, helps prevent the return of symptoms.
2. Ice Therapy
Reducing Inflammation: Regular application of ice packs to the affected area can significantly decrease swelling and pain, aiding in the recovery process.
3. Compression Techniques
Swelling Reduction: Using compression garments around the lower leg can help minimize swelling and provide support, enhancing the healing environment.
4. Medication for Symptom Relief
NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can offer relief from pain and inflammation, with adherence to prescribed usage ensuring safety and effectiveness.
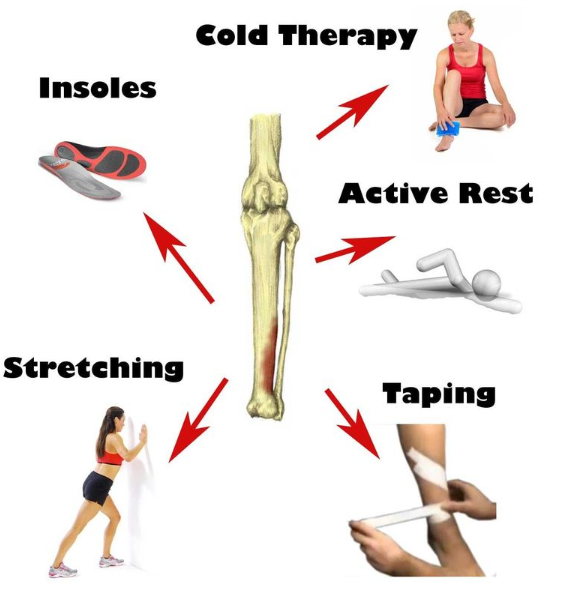
5. Physical Therapy and Exercises
Muscle Conditioning: Tailored physical therapy programs focus on stretching and strengthening the shin area, promoting recovery and preventing future injuries.
6. Orthotic Support
Custom Foot Support: Orthotics can be crucial for individuals with specific foot structures, providing the support needed to distribute weight more evenly and reduce stress on the shin.

Prevention
1. Progressive Training Adaptation
Measured Activity Enhancement: Carefully increasing the intensity and volume of exercises allows the legs to adapt safely, reducing the risk of shin splints.
Incorporating Rest Days: Rest is integral to recovery, helping to avert excessive strain on the shinbone and tissues.
2. Optimal Footwear Selection
Activity-Specific Shoes: Choosing footwear with adequate support and cushioning, tailored to your activities, is key in preventing shin splints.
Professional Shoe Fitting: Expert fitting advice ensures shoes are well-suited to your foot type and activity style.
3. Varied Exercise Routines
Activity Variation: A balanced mix of high and low-impact exercises distributes physical stress more evenly, protecting the shin area.
4. Effective Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
Preparation and Recovery: Starting with dynamic stretches and ending with static stretches prepares the body for activity and aids in muscle recovery, respectively.
5. Targeted Strengthening and Flexibility Exercises
Muscle Support: Exercises aimed at strengthening the shin and surrounding muscles improve stability and reduce the likelihood of shin splints.
Maintaining Flexibility: Regular stretching of the lower leg muscles ensures flexibility, helping to prevent the conditions that lead to shin splints.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are shin splints?
Shin splints refer to pain along the shinbone, typically caused by overuse of leg muscles, tendons, and bone tissue during physical activities.
Q2: What causes shin splints?
The main causes include excessive physical activity, improper footwear, biomechanical factors, muscle imbalances, and engaging in activities on hard or irregular surfaces.
Q3: How can I alleviate shin splint pain?
Effective strategies include rest and recovery, ice therapy, compression techniques, medication for symptom relief, physical therapy, and using orthotic support.
Q4: How can I prevent shin splints?
Preventive measures include progressive training adaptation, incorporating rest days, choosing activity-specific shoes, varied exercise routines, and effective warm-up and cool-down routines.
Q5: When should I see a doctor for shin splints?
If the pain persists despite self-care measures, or if it significantly hinders daily activities, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Conclusion
Shin splints, while common, should not be a recurring barrier to your physical activities. By understanding their causes, recognizing symptoms early, and implementing effective treatment and prevention strategies, you can maintain healthy, pain-free legs. Remember, the key to overcoming shin splints lies in a balanced approach to physical activity, proper footwear, and attentive self-care. Stay informed, stay healthy, and keep moving forward on your fitness journey.

MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers