Unlock a comprehensive guide to understanding warts, from identifying different types to exploring effective treatments and preventive measures. Dive into expert advice on managing the physical and emotional impacts of warts, enhancing your well-being.
Introduction
Warts, those pesky, non-cancerous skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), are more than just a physical nuisance. They carry a stigma that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. This guide delves into the types of warts, their causes, and the spectrum of treatments available, from over-the-counter remedies to professional medical interventions. We also explore lifestyle adjustments and natural remedies for prevention and care, alongside strategies to cope with the psychological impact of wart.
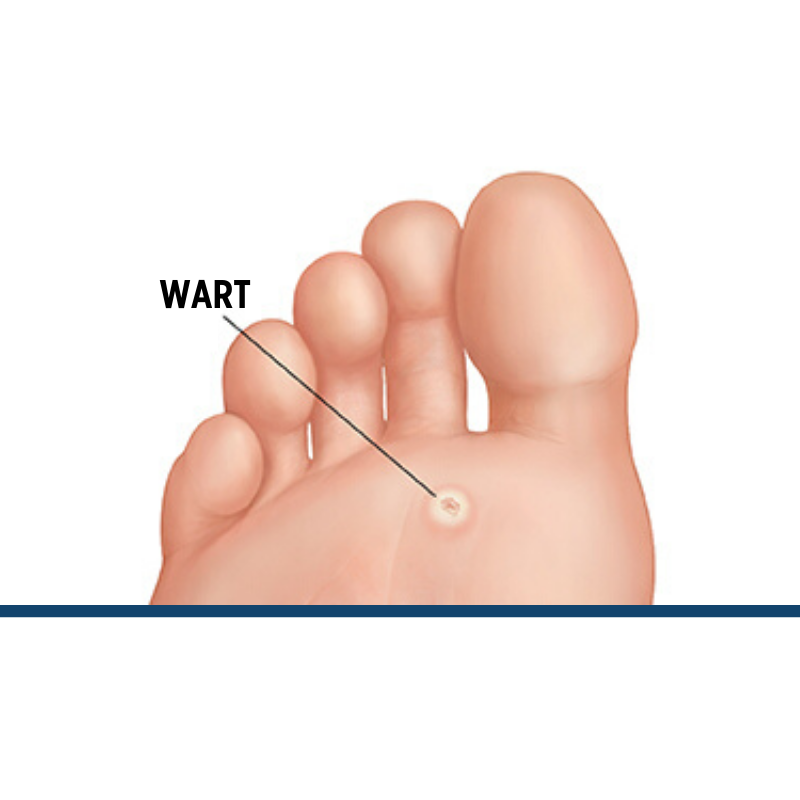
Table of Contents
What is Wart?
Wart is non-cancerous skin growths triggered by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These growths can appear on various body parts, with a higher prevalence on the hands, feet, and face. Due to their contagious nature, wart can spread through direct skin contact or by touching objects contaminated with the virus.
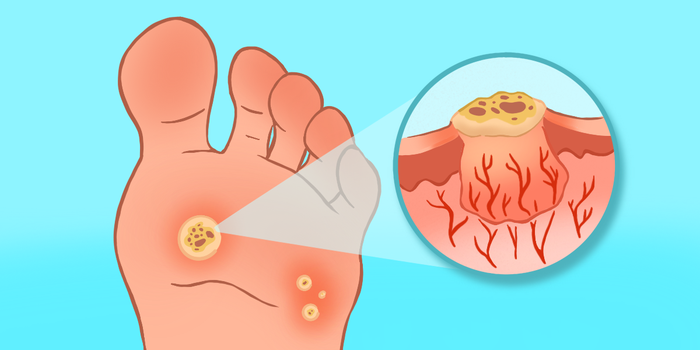
Different Types of Warts

1. Common Wart (Verruca Vulgaris)
Appearance: Rough, cauliflower-like texture, appearing as raised bumps.
Location: Typically found on hands, fingers, and elbows where skin frequently breaks.
Symptoms: Generally painless but can cause discomfort due to their appearance or if located in areas of frequent movement.
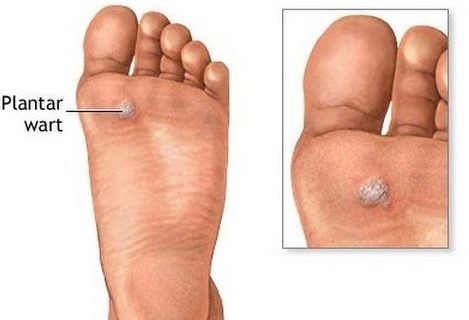
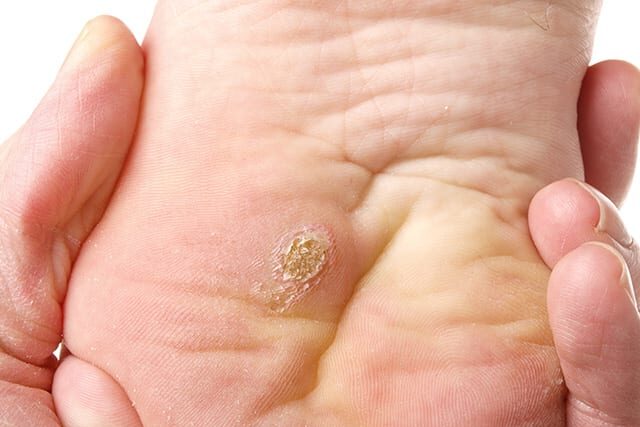
2. Plantar Wart (Verruca Plantaris)
Appearance: Hard, grainy growths on the foot’s sole with a central black dot from clotted blood vessels.
Location: Sole of the foot, especially under pressure points like heels or balls of the feet.
Symptoms: Can be painful, resembling the sensation of stepping on pebbles. The pressure from walking or standing may push them inward, complicating mobility.
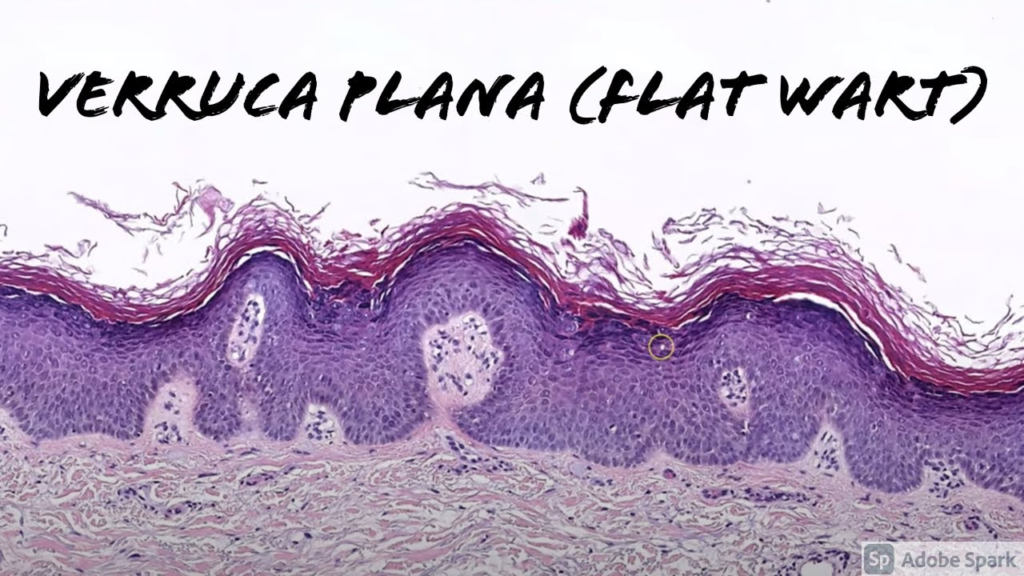
3. Flat Wart (Verruca Plana)
Appearance: Smaller, smoother, and flatter than other wart, often appearing in clusters.
Location: Commonly found on the face, thighs, or arms.
Symptoms: Mostly painless but can cause cosmetic concerns and occasional itching due to their number and visibility.
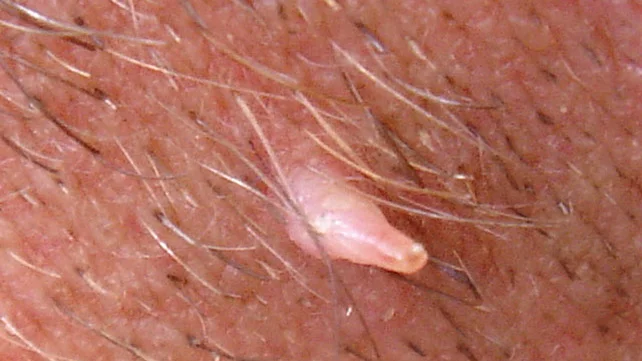
4. Filiform Wart
Appearance: Notable for their long, thread-like projections.
Location: Predominantly grow on the face, such as around the mouth, nose, and eyes, where they are most noticeable.
Symptoms: Rapid growth can lead to discomfort and significant cosmetic concern due to their prominent facial location.
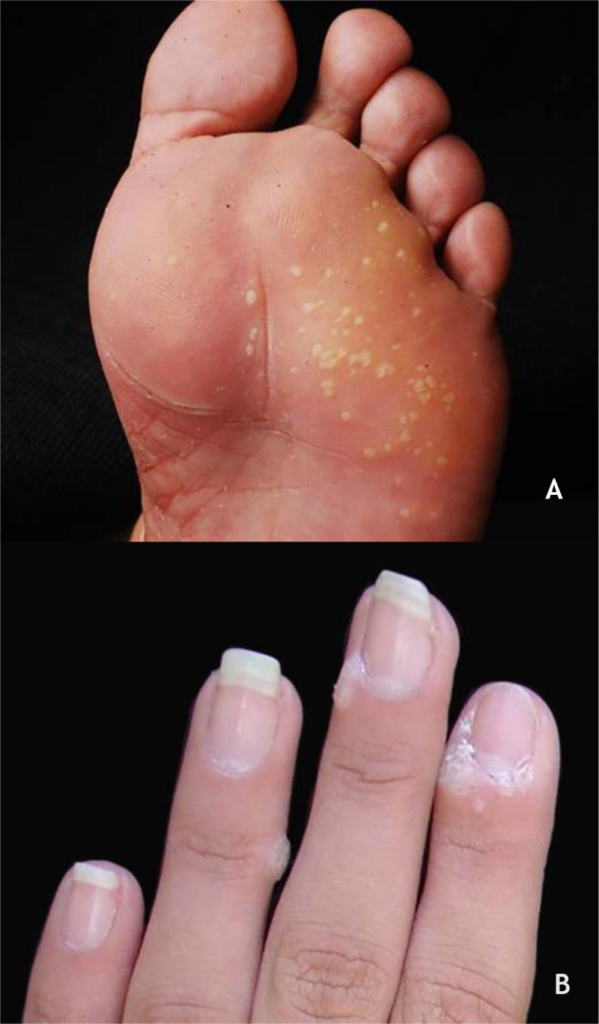
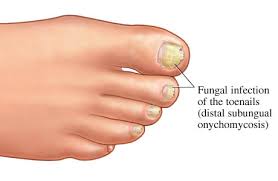
5. Periungual Wart
Appearance: Rough-textured wart that can disrupt nail growth.
Location: Appear around or under toenails and fingernails, potentially growing under the nail bed.
Symptoms: Periungual wart can be painful and may lead to nail deformities, detachment, or fungal infections without proper treatment.
Understanding the different types of warts is crucial for identifying and seeking appropriate treatment, especially for those that cause pain, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns.
Understanding the Risk Factors for Wart Development
Wart, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), can affect anyone but certain conditions and behaviors increase the likelihood of developing them. Recognizing these risk factors is crucial for prevention and early treatment.
Key Risk Factors for Wart:
| Compromised Skin Integrity: Activities that lead to skin damage, such as shaving, create entry points for HPV. It’s essential to exercise caution and protect the skin from cuts and abrasions. |
| Direct Contact: HPV spreads through direct contact with a wart on another person or through autoinoculation, which occurs when the virus is spread from one part of the body to another. Sharing personal items like towels or razors can also facilitate transmission. |
| Immune System Health: Individuals with weakened immune systems, due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or immune-suppressing medications, are at a higher risk of developing wart. |
| Age Factors: Younger individuals, particularly children and teenagers, are more susceptible to wart. This vulnerability is often due to more frequent skin injuries and an immune system that’s still developing. |
| Moist Environments: HPV thrives in warm, moist conditions. Walking barefoot in communal areas such as showers, locker rooms, or around pools can increase the risk of contracting plantar wart. |
Identifying Wart: Characteristics and Symptoms
Early identification of warts is possible by noting their distinct features and understanding how they manifest on the skin.
Characteristics of Wart:
| Texture and Color: Wart often have a rough texture and can be the same color as your skin or slightly darker. They may appear smooth or bumpy to the touch. |
| Black Dots: These are not “seeds” but clotted blood vessels that supply the wart. They are a common feature of many warts. |
| Pain and Discomfort: While many warts are painless, those in areas subject to pressure or friction (like the soles of the feet) can be uncomfortable or painful. |
| Growth and Spread: Wart can grow in size and number. Plantar wart, for example, may cluster together in a mosaic-like pattern. |
Awareness of these risk factors and characteristics can aid in the prevention and early detection of wart, facilitating timely and effective treatment.
Solutions and Strategies for Managing Wart
Wart, while often harmless, can be a source of discomfort and self-consciousness. Understanding the range of treatments and preventive measures can empower individuals to manage and potentially eliminate wart effectively.
Over-the-Counter Remedies and Professional Treatments
- Salicylic Acid Applications: Available as liquids, gels, or adhesive patches, salicylic acid aids in gradually peeling away the wart. Enhancing its effectiveness involves soaking the wart in warm water and gently removing dead tissue with a file.
- Home Cryotherapy Kits: Offering a DIY approach to freezing wart, these kits must be used with caution to avoid damaging surrounding skin.
Seeking Professional Care
- Cryotherapy: A dermatologist applies liquid nitrogen to freeze the wart, which typically falls off after forming a blister. Multiple sessions are often required for complete removal.
- Cantharidin Application: Known colloquially as “beetle juice,” this substance causes the wart to blister and detach from the skin.
- Surgical and Laser Removal: For persistent warts, surgical excision or laser therapy may be recommended to directly remove or destroy the wart tissue.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment enhances the body’s immune response to HPV, potentially clearing wart through the application of topical agents or systemic medications.
Lifestyle and Natural Remedies for Prevention and Care
Incorporating lifestyle changes and exploring natural remedies can complement traditional treatments and help prevent wart recurrence.
Preventive Lifestyle Measures
Boost Immune Health: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can strengthen the immune system.
Skin Care and Hygiene: Keeping the skin clean and dry, especially in communal and moist environments, is crucial for preventing wart.
Protective Measures: Wearing appropriate clothing and avoiding direct contact with wart can minimize the risk of spread.
Natural Treatment Options
Tea Tree Oil: Its antiviral properties may reduce wart size when applied topically in a diluted form.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Thought to work similarly to salicylic acid, it should be used cautiously due to its potential for skin irritation.
Garlic: The antimicrobial effects of garlic may be beneficial when applied directly to the wart and covered overnight.
Aloe Vera: Applying aloe vera gel directly to the wart might soothe the skin and aid in treatment due to its antiviral components.
Dietary Adjustments: Incorporating foods high in zinc and vitamins C and E can support skin health and the immune system.
Addressing the Psychological Impact of Warts
The presence of warts can be more than just a physical nuisance; it can carry a heavy emotional burden, affecting how individuals view themselves and their interactions with others.
Coping Strategies for the Emotional Impact of Warts
Seeking Community and Professional Support: Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide a sense of comfort and belonging. Online forums and support groups can be excellent sources of advice and empathy.
Educating Yourself and Sharing Knowledge: Understanding that warts are common and generally harmless can alleviate some of the anxiety associated with them. Educating those around you can help reduce misconceptions and stigma, promoting a more supportive environment.
Focusing on What You Can Control: Direct your energy towards actionable steps like pursuing treatment and taking care of your mental health. Recognizing what aspects you can influence can help regain a sense of empowerment.
Prioritizing Self-Care: Engaging in activities that boost your self-esteem and reduce stress is crucial. Whether it’s through hobbies, exercise, or relaxation techniques, find what brings you happiness and peace.
Consulting with Professionals: If warts significantly impact your quality of life, seeking advice from dermatologists for treatment options and mental health professionals for coping strategies is crucial. Professional guidance can offer tailored solutions and support for navigating both the physical and emotional challenges of warts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What causes warts?
A: Warts are caused by different strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV) and can spread through direct contact with a wart or something that touched a wart.
Q: Are warts contagious?
A: Yes, warts are contagious. They can spread from person to person or through contact with objects that have come into contact with a wart.
Q: What are the common types of warts?
A: The most common types include common warts, plantar warts, flat warts, filiform warts, and periungual warts, each with unique characteristics and preferred locations on the body.
Q: How can I prevent warts?
A: Preventive measures include maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, and making lifestyle adjustments to boost your immune system.
Q: What treatments are available for warts?
A: Treatments range from salicylic acid and cryotherapy kits to professional options like cryotherapy, cantharidin, surgical methods, and immunotherapy.
Conclusion
Warts, while common, don’t have to be a permanent or distressing part of your life. With a clear understanding of their types, risk factors, and the array of treatment options available, you can take proactive steps towards prevention and management. Remember, the journey to overcoming warts is not just about treating the physical symptoms but also addressing the emotional impact. By embracing a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, natural remedies, and seeking support, you can navigate the challenges of warts with confidence and resilience.

MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers