Discover the secrets to managing Raynaud’s Phenomenon for healthier feet. Learn about symptoms, types, and effective strategies to enhance your quality of life. Dive into our comprehensive guide now.
What Exactly is Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
Raynaud’s Phenomenon is identified by a temporary decrease in blood flow to certain body parts, predominantly the fingers and toes. Triggered by exposure to cold or emotional stress, this diminished blood flow can cause noticeable alterations in the color and feeling in the impacted regions.
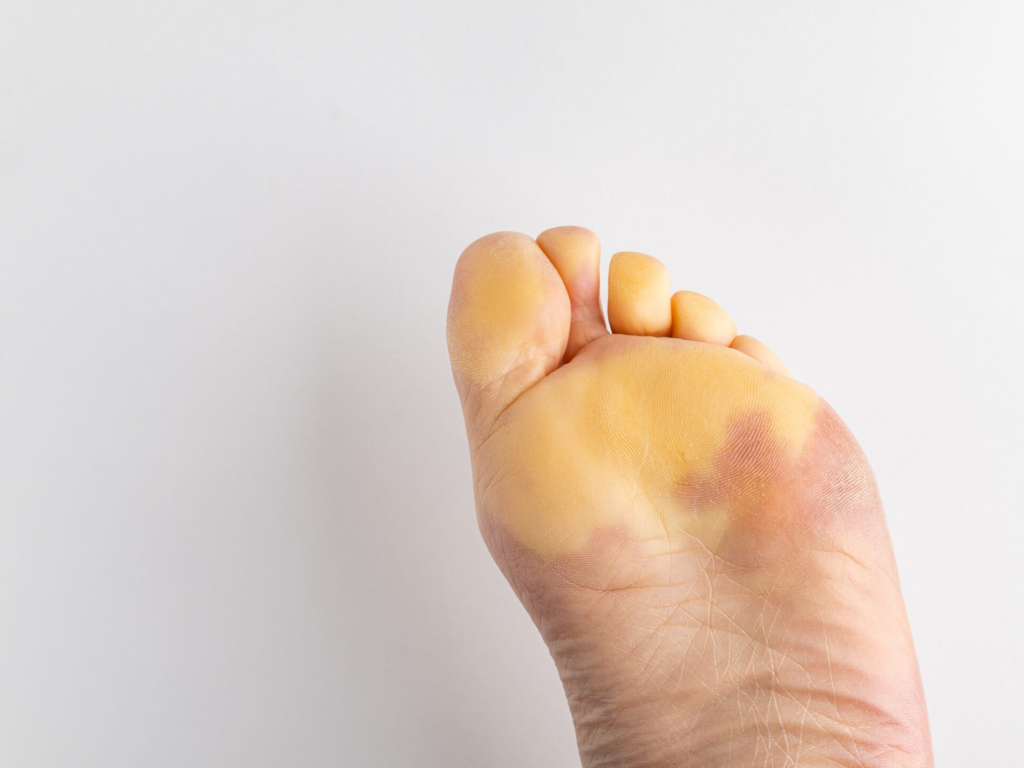
Table of Contents
Understanding the Types of Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Raynaud’s Phenomenon manifests in two primary forms, each with its unique set of characteristics, causes, and management strategies. Recognizing the differences between these types is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Here’s a closer look at the two classifications:
1. Primary Raynaud’s Phenomenon (Also Known as Raynaud’s Disease)
- Characteristics: This variant is the more prevalent form of Raynaud’s, occurring independently of any other medical conditions. Symptoms are generally mild and can be managed effectively.
- Causes: The exact origins of primary Raynaud’s remain unclear, though it’s believed to involve disruptions in the nervous system’s regulation of blood vessel constriction and dilation.
- Management: Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining warmth, minimizing stress, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine and nicotine, are often sufficient. In more severe instances, medications to widen blood vessels may be prescribed.
2. Secondary Raynaud’s Phenomenon (Raynaud’s Syndrome)
- Characteristics: This less common but more severe form is associated with other underlying health issues, particularly autoimmune or connective tissue diseases.
- Causes: Secondary Raynaud’s can arise from conditions such as scleroderma, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren’s syndrome. It may also be triggered by physical injuries, chemical exposure, or certain medications that impair blood flow.
- Management: Treatment targets the root cause and may include lifestyle adjustments, medication, and possibly surgery to enhance blood circulation.

Key Differences
- Severity: Secondary Raynaud’s is typically more severe than its primary counterpart, carrying a greater risk of complications like skin ulcers or gangrene.
- Symptoms: Both types can lead to changes in skin color, numbness, tingling, and pain in affected areas, but secondary Raynaud’s symptoms are often more severe and long-lasting.
- Treatment Approach: While primary Raynaud’s can usually be managed with simple lifestyle changes and sometimes medication, secondary Raynaud’s treatment is more complex, focusing on the underlying health issue.
For those experiencing Raynaud’s Phenomenon symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for obtaining an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention is particularly important for those with secondary Raynaud’s to avoid serious complications and enhance overall quality of life.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon and Its Impact on the Feet
Raynaud’s Phenomenon can have a profound effect on the feet, leading to symptoms that range from mild discomfort to severe pain and even complications. A deeper understanding of these symptoms is essential for early recognition and effective management of the condition. Here’s an in-depth look at the impact of Raynaud’s Phenomenon on the feet:
Color Changes
Phases of Color Transition: During a Raynaud’s episode, the feet undergo three distinct color changes—white, blue, and red—each indicating a different phase of blood flow disruption and recovery. The initial white phase signifies reduced blood flow, followed by a blue phase indicating oxygen depletion. The final red phase occurs as blood flow resumes, often accompanied by throbbing or a burning sensation.
Visual Signs: These color shifts are key indicators of Raynaud’s, triggered by cold exposure or stress, and can last from minutes to hours.
Sensation Changes
Numbness and Tingling: Decreased blood flow can cause a “pins and needles” sensation, leading to numbness and tingling in the feet.
Pain: Pain, ranging from mild to severe, may occur, particularly as blood flow returns during the reperfusion phase, impacting mobility and daily life.
Temperature Sensitivity
Cold Sensitivity: Those with Raynaud’s often experience heightened sensitivity to cold, leading to more frequent and intense episodes in lower temperatures or air-conditioned settings.
Adaptive Strategies: Wearing thermal socks, using foot warmers, and avoiding cold surfaces are necessary measures to manage this sensitivity.
Ulcers and Sores
Ulcer Formation: Severe or frequent Raynaud’s episodes can lead to ulcers or sores on the feet due to prolonged blood flow reduction, making the skin prone to damage and infection.
Healing Difficulties: Healing these ulcers can be challenging due to poor circulation, increasing the risk of infection and necessitating specialized care.
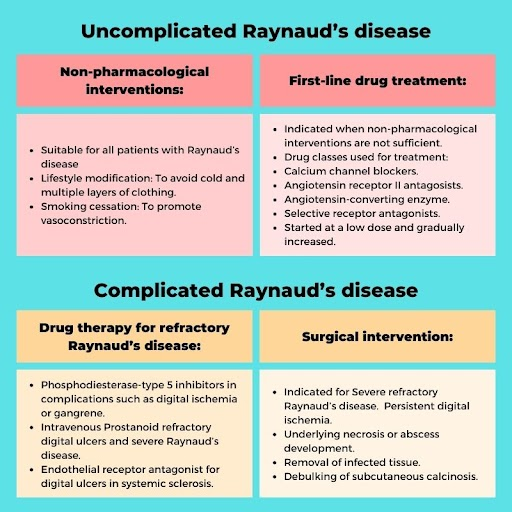
Strategies for Managing Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Effective management of Raynaud’s involves lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and self-care techniques aimed at alleviating symptoms and minimizing the occurrence of episodes. Below are key strategies for managing the condition:
Stay Warm
| Layering Clothes Dressing in multiple layers helps retain body heat more efficiently than a single thick layer by trapping warm air close to the skin. |
| Appropriate Footwear Opt for insulated, waterproof shoes during cold weather and wear wool or thermal socks for added warmth. |
| Regulating Environment Ensure living and workspaces are well-heated. Utilize insulated curtains, draft blockers, and carpets to keep heat in. A heated blanket or mattress pad can also be beneficial at night. |
| Warm Water Soaks Immersing feet in warm (not hot) water can quickly relieve symptoms by restoring blood flow during an episode. |
Stress Reduction Techniques
| Mindfulness and Relaxation Engaging in mindfulness meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can significantly lower stress levels, potentially reducing the frequency of Raynaud’s episodes. |
| Effective Time Management Organizing your daily schedule to avoid rushing and stress, prioritizing tasks, and incorporating breaks can foster a more relaxed mindset. |
| Professional Support For those overwhelmed by stress, consulting with a psychologist or counselor can offer effective strategies for stress management. |
Smoking Cessation Strategies
| Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) Utilizing gum, patches, or lozenges can aid in managing nicotine cravings, facilitating the quitting process. |
| Support Programs Participation in support groups or smoking cessation programs offers motivation and support essential for quitting. |
| Healthcare Consultation A healthcare provider can prescribe medications or recommend treatments specifically designed to assist in quitting smoking. |
Regular Exercise Regimen
| Customized Exercise Plan Collaborate with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to create an exercise routine tailored to your needs. Opt for low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling. |
| Proper Warm-Up A comprehensive warm-up is crucial to prevent Raynaud’s attacks, especially in cooler conditions. Keep your body adequately warm during physical activity. |
| Consistent Exercise Engaging in regular, moderate exercise enhances circulation and overall health, diminishing the intensity of Raynaud’s symptoms over time. |
Medication Options
| Calcium Channel Blockers These medications are effective in relaxing and widening small blood vessels in the hands and feet, alleviating the severity and frequency of attacks. |
| Vasodilators Drugs that expand blood vessels, such as topical nitroglycerin ointment, can aid in healing skin ulcers on fingers or toes. |
| Antihypertensive Medications Certain high blood pressure medications can also be beneficial in managing Raynaud’s symptoms. |
Additional Tips
| Dietary Considerations Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, as these can provoke Raynaud’s episodes, may help in symptom management. |
| Protecting Extremities Always wear gloves and warm socks in cold or refrigerated settings. Electronic hand and foot warmers offer extra warmth. |
| Handling Stress-Induced Symptoms For individuals where emotional stress triggers episodes, employing biofeedback and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be effective in managing these stress-induced symptoms. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What exactly is Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
A: Raynaud’s Phenomenon is a condition marked by a temporary reduction in blood flow to certain parts of the body, mainly the fingers and toes, often triggered by cold temperatures or stress.
Q: How does Raynaud’s Phenomenon affect the feet?
A: It can cause changes in skin color, numbness, tingling, and pain in the feet, impacting daily activities and overall foot health.
Q: What are the types of Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
A: There are two types: Primary Raynaud’s, which occurs independently of other conditions, and Secondary Raynaud’s, which is associated with underlying health issues.
Q: Can Raynaud’s Phenomenon lead to complications?
A: Yes, especially in cases of Secondary Raynaud’s, complications like skin ulcers or gangrene can occur without proper management.
Q: What strategies can help manage Raynaud’s Phenomenon?
A: Strategies include staying warm, reducing stress, quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and, in some cases, medication.
Conclusion
Managing Raynaud’s Phenomenon, particularly its effects on the feet, requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medical treatment, and self-care techniques. By staying informed and proactive, individuals affected by Raynaud’s can lead healthier, more comfortable lives. Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. With the right strategies, the impact of Raynaud’s on your feet and your overall well-being can be significantly minimized.
| Arch Support |
| Arch Supports |
| Best Arch Support Insoles |
| Best Insole for Plantar Fasciitis |
| Insole for Flat Feet |


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers