When it comes to muscle recovery, timing and nutrition play a significant role. Among the wide array of protein options, casein protein stands out as a slow-digesting powerhouse, perfect for night-time recovery. In this article, we will explore why casein protein is highly regarded by fitness enthusiasts and athletes alike, and how it can optimize your overnight muscle repair and growth.
Table of Contents
What Is Casein Protein?
Definition of Casein Protein
Casein protein is a slow-digesting protein primarily found in dairy products. It constitutes around 80% of the protein in cow’s milk, with the remaining 20% made up of whey protein. Unlike fast-digesting proteins, casein forms a gel-like substance in the stomach, leading to a prolonged release of amino acids over several hours. This makes it an excellent choice for providing the body with a sustained source of nutrients, particularly when the body is fasting, such as during sleep.

Where Does Casein Come From?
Casein is derived from milk, specifically cow’s milk, and is obtained through a process that separates the solid proteins from the liquid whey. It is a naturally occurring protein in many dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt. The solid component of milk, known as curds, is primarily composed of casein, which is why cheese, in particular, is so rich in this protein.
Types of Casein (Micellar Casein vs. Casein Hydrolysate)
There are two main types of casein protein found in supplements:
- Micellar Casein: This is the most common form of casein found in supplements. It is the purest and least processed version, allowing it to digest slowly over time. When consumed, it forms micelles in the stomach, which are clusters of protein molecules that take longer to break down, providing a steady release of amino acids.
- Casein Hydrolysate: This type of casein is partially broken down, or hydrolyzed, for faster digestion. While it still digests slower than whey protein, it is absorbed quicker than micellar casein. Casein hydrolysate is often used in clinical nutrition or by athletes looking for a more immediate release of nutrients without compromising too much on the slow-release properties.
How Casein Protein Works in the Body
Slow Digestion Process Explained
The defining characteristic of casein protein is its slow digestion rate. After consumption, casein forms a gel or clot in the stomach, which takes longer to digest compared to other proteins like whey. This process leads to a slower release of amino acids into the bloodstream, providing your muscles with a constant supply of nutrients over several hours. It can take up to 7-8 hours for casein to be fully digested and absorbed, making it ideal for periods when your body goes without food, such as overnight.
Amino Acid Release Over Several Hours
Because of its slow-digesting nature, casein offers a prolonged release of amino acids, the building blocks of protein, into your bloodstream. This continuous release helps in preventing muscle breakdown, supporting muscle repair and growth over an extended period. Unlike whey protein, which floods your system with amino acids in a short time, casein ensures that your muscles have access to a steady supply of these essential nutrients.
Comparison to Fast-Digesting Proteins Like Whey
Whey protein, another popular protein, digests rapidly, making it a great post-workout supplement when your body needs immediate recovery. In contrast, casein’s slow digestion makes it a superior option for night-time use, as it ensures a longer-lasting nutrient supply. Essentially, whey is like a quick energy boost, while casein acts more like a slow-drip feed, keeping your body nourished for longer periods.
Why Casein Protein Is Ideal for Night-Time Recovery
Muscle Repair During Sleep
During sleep, your body enters a state of recovery, repairing muscles that have been stressed or damaged throughout the day. Since you’re fasting for several hours while asleep, your muscles need a constant supply of amino acids to fuel this repair process. Casein protein ensures that your muscles have a steady stream of amino acids all night long, promoting muscle repair and reducing the risk of muscle breakdown.
The Role of Casein in Preventing Muscle Breakdown (Catabolism)
Catabolism, or muscle breakdown, occurs when the body doesn’t have enough nutrients to sustain muscle mass, especially during fasting periods like sleep. Casein protein’s slow digestion helps combat catabolism by continuously delivering amino acids to the muscles, thus preserving muscle tissue and promoting recovery. It is especially beneficial for athletes or those trying to gain or maintain muscle mass during calorie deficits.
Scientific Studies Supporting Night-Time Casein Consumption
Several studies have backed up the effectiveness of consuming casein before bed. Research shows that casein protein can increase muscle protein synthesis overnight and help prevent muscle loss. One study found that athletes who consumed casein protein before sleep experienced significantly better muscle recovery and strength gains compared to those who didn’t. Another study confirmed that casein consumption before bed could enhance muscle repair and recovery without leading to fat gain.
Casein vs. Whey: The Key Differences
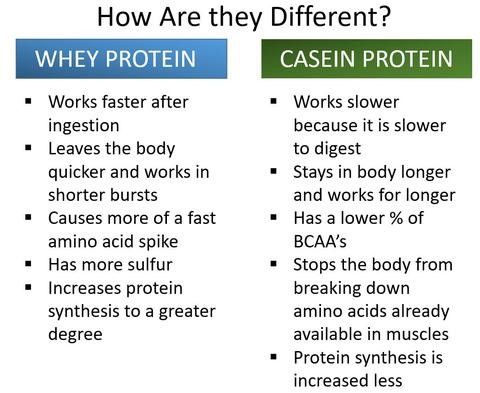
While both casein and whey come from milk, they serve different purposes. Whey is a fast-digesting protein, making it ideal for post-workout recovery when your muscles need immediate replenishment. Casein, on the other hand, is slow-digesting, making it perfect for night-time consumption.
Key Differences:
- Digestion Speed: Whey digests in about 1-2 hours, while casein takes up to 7-8 hours.
- Usage Timing: Whey is best for post-workout, while casein is optimal before bed.
- Muscle Protein Synthesis: Both support muscle growth, but casein excels at preventing muscle breakdown during long periods of fasting.
Benefits of Casein Protein
- Sustained Muscle Growth: The slow release of amino acids helps keep your muscles in a positive protein balance for an extended period.
- Enhanced Overnight Recovery: By providing a steady nutrient supply while you sleep, casein boosts recovery, making sure you wake up stronger.
- Supports Fat Loss: Casein promotes fat loss by preserving muscle mass during calorie restriction.
- Prevents Muscle Breakdown: Its slow-digesting nature is perfect for preventing muscle catabolism, particularly during extended fasting periods like sleep.
How to Take Casein Protein
For best results, it’s recommended to take casein protein 30 minutes to an hour before bed. This timing ensures that the slow release of amino acids coincides with your body’s natural recovery process during sleep. The recommended dosage is typically 20-40 grams, depending on your goals—whether you’re aiming for muscle growth, fat loss, or maintenance.
Casein is available in various forms, including powders, ready-to-drink shakes, and bars, making it easy to incorporate into your routine.
Natural Sources of Casein Protein

If you prefer to get your casein from whole foods rather than supplements, dairy products are a great option. Foods rich in casein include:
- Milk
- Yogurt
- Cheese (especially cottage cheese)
Incorporating these foods into your evening meals or snacks can help boost your casein intake naturally.
Casein Protein for Athletes and Bodybuilders
Why Athletes Need Slow-Releasing Proteins
Athletes undergo intense physical training that breaks down muscle fibers, requiring continuous nutrient supply for optimal recovery. Slow-releasing proteins like casein are crucial because they help maintain an anabolic state (muscle-building state) for longer periods, especially during sleep when the body is fasting. This is essential for maximizing recovery and muscle growth, particularly in athletes who are training multiple times a day or who follow strict calorie-controlled diets.
Importance of Casein in Competitive Sports and Bodybuilding
In competitive sports and bodybuilding, muscle recovery and growth are key to performance. Casein helps athletes meet their protein needs without the risk of muscle catabolism. Because of its slow digestion, casein supports sustained muscle recovery, even during periods of prolonged rest. Many bodybuilders rely on casein protein for overnight recovery to ensure that they wake up without muscle loss, keeping their hard-earned gains intact.
Success Stories of Athletes Using Casein for Recovery
Many professional athletes and bodybuilders incorporate casein protein into their nightly routine to enhance their recovery. Numerous case studies and personal testimonies highlight the significant improvements in strength, recovery times, and muscle maintenance for those who consistently consume casein before bed. Athletes report fewer injuries, faster recovery, and better overall performance thanks to this slow-digesting protein.
Casein Protein for Weight Loss
How Casein Aids in Fat Loss
While casein is known for supporting muscle growth, it also plays a significant role in fat loss. Because it digests slowly, casein helps increase feelings of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake and preventing late-night snacking. This makes it easier to stick to a calorie-restricted diet while maintaining muscle mass, which is essential for burning fat efficiently.
Satiety and Its Role in Reducing Late-Night Cravings
One of the key benefits of casein is that it keeps you feeling full for longer periods. This extended feeling of satiety can help curb late-night cravings, which is often a challenge for people trying to lose weight. By reducing hunger and maintaining steady energy levels, casein makes it easier to avoid unhealthy snacks before bed, supporting weight management goals.
Benefits for Those on a Calorie Deficit Diet
For individuals on a calorie deficit, preserving muscle mass while losing fat is a top priority. Casein protein helps by providing a steady supply of amino acids that protect muscle tissue during weight loss. Since muscle mass is key to boosting metabolism and burning fat, casein supports a leaner, more toned physique by preserving muscle even when overall caloric intake is reduced.
Common Myths About Casein Protein

- Does Casein Cause Bloating?
Casein, like any dairy product, can cause bloating in individuals who are lactose intolerant, but for most people, it is well-tolerated. - Is Casein Only for Bodybuilders?
While bodybuilders often use casein, it’s beneficial for anyone looking to support muscle recovery and growth, especially during night-time. - Does Casein Cause Weight Gain?
Casein alone does not cause weight gain; overconsumption of calories in general leads to weight gain.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While casein is safe for most people, those with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies should be cautious. If you experience digestive issues after consuming casein, consider switching to a lactose-free or plant-based protein alternative.
How to Choose the Best Casein Protein Supplement
When shopping for casein supplements, look for products that use micellar casein, as it’s the purest form. Check the ingredient list to avoid unnecessary additives or fillers. Organic and grass-fed casein options may offer a cleaner source of protein.
Casein and Sleep Quality
Interestingly, some studies suggest that casein might help improve sleep quality. The protein provides a sense of satiety, which can prevent waking up hungry during the night. Pairing casein with other sleep-supportive nutrients like magnesium could further enhance your night’s rest.
Conclusion
Casein protein is a unique, slow-digesting protein that plays a critical role in overnight muscle recovery and growth. By providing a steady release of amino acids over several hours, it ensures that your body has the nutrients it needs while you sleep. Whether you’re aiming to build muscle, lose fat, or simply maintain your current physique, casein can be a powerful addition to your routine.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is casein protein safe for everyone?
Yes, but individuals with dairy allergies or lactose intolerance should exercise caution.
Can I take casein if I’m lactose intolerant?
Some casein supplements are low in lactose, but it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider or choose lactose-free alternatives.
How long does casein take to digest fully?
Casein can take up to 7-8 hours to fully digest, making it ideal for night-time use.
Is casein more effective than whey for muscle growth?
Both are effective, but casein is superior for long-term protein supply, especially overnight.
Can casein help improve sleep quality?
Yes, its slow digestion may help reduce hunger during the night and promote better sleep.



MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers