In recent years, pea proteins have skyrocketed in popularity, particularly among those looking for plant-based alternatives to traditional animal-derived proteins. With the rise of veganism and increasing awareness of sustainable eating, more people are seeking out protein sources that are both healthy and environmentally friendly. But is pea protein truly the best plant-based protein alternative available? In this article, we’ll dive deep into everything you need to know about pea proteins, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and how it compares to other protein options.
Table of Contents
What is Pea Protein?
The Basics of Pea Protein
Pea protein is derived from yellow split peas, a legume that has been a staple in diets around the world for centuries. Unlike whole peas, which are rich in carbohydrates and fiber, pea protein is made by extracting the protein content from the peas, creating a concentrated protein powder. This powder is widely used in protein supplements, snacks, and even some meal replacement products.
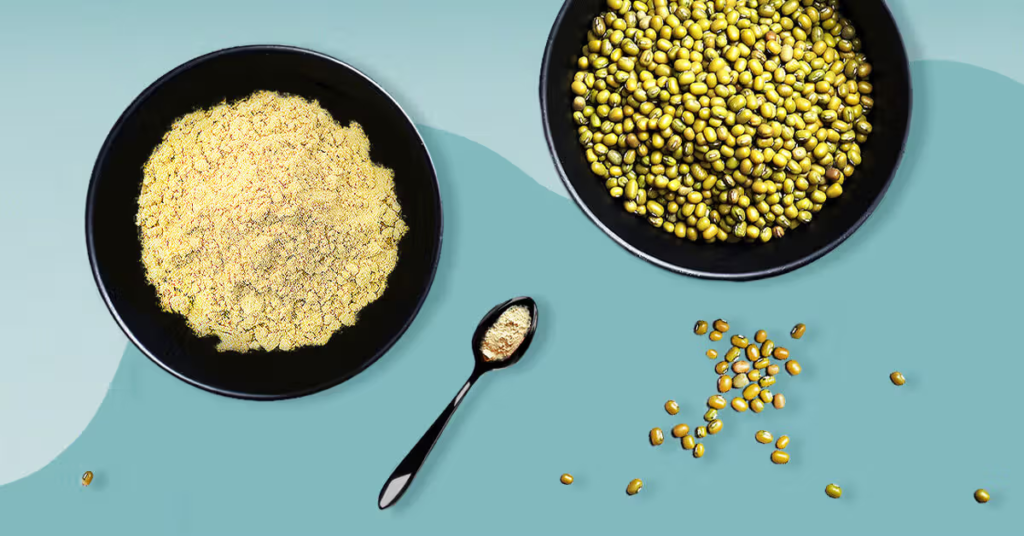

How Pea Protein is Made
The process of creating pea protein involves milling yellow peas into a fine powder, removing the starch and fiber, and isolating the protein. The result is a protein powder that is relatively low in fat and carbohydrates but rich in protein. Depending on the processing, pea protein can be classified as either pea protein concentrate or pea protein isolate. Isolates tend to have a higher protein content—sometimes as much as 85-90%—while concentrates usually contain slightly less.
Types of Pea Protein: Isolate vs. Concentrate
Pea protein isolate is more refined, offering a purer form of protein, while pea protein concentrate contains more of the other natural components of peas, such as fiber. Depending on your nutritional needs and how you plan to use it, you might choose one type over the other. For example, isolates are often preferred for muscle building, while concentrates may be a good option if you’re seeking a more natural, whole-food-based protein supplement.
Why Choose Pea Proteins Over Other Plant-Based Proteins?

Pea Proteins vs. Soy Proteins
Soy protein has long been a popular choice among plant-based enthusiasts, but it has a few downsides. For one, soy is a common allergen, making it unsuitable for those with soy allergies or intolerances. Moreover, concerns about phytoestrogens in soy products, which may mimic estrogen in the body, have driven some people to seek out alternatives like pea protein. Pea protein, on the other hand, is hypoallergenic and free from these concerns.
Pea Proteins vs. Rice Proteins
Rice protein is another plant-based option, but it tends to have a lower overall protein content and lacks certain essential amino acids, making it an incomplete protein. Pea protein, however, is much closer to being a complete protein, as it contains all nine essential amino acids. When compared directly, pea protein has a higher protein content and a better amino acid profile than rice protein, making it the superior choice for those seeking optimal nutrition.
Pea Proteins vs. Hemp Proteins
Hemp protein is another trendy plant-based option, but it falls short in certain areas. While hemp protein is rich in healthy fats and fiber, its protein content is significantly lower than pea protein. If your primary goal is to increase your protein intake, especially for fitness or muscle gain, pea protein is the better option. Hemp is more suited for those looking for a broader nutritional profile that includes fats and fiber, in addition to protein.
Health Benefits of Pea Proteins
Rich Source of Essential Amino Acids
One of the major benefits of pea protein is its amino acid profile. While not 100% complete like animal-based proteins, it does contain all nine essential amino acids, including high levels of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These amino acids are particularly important for muscle repair and growth.
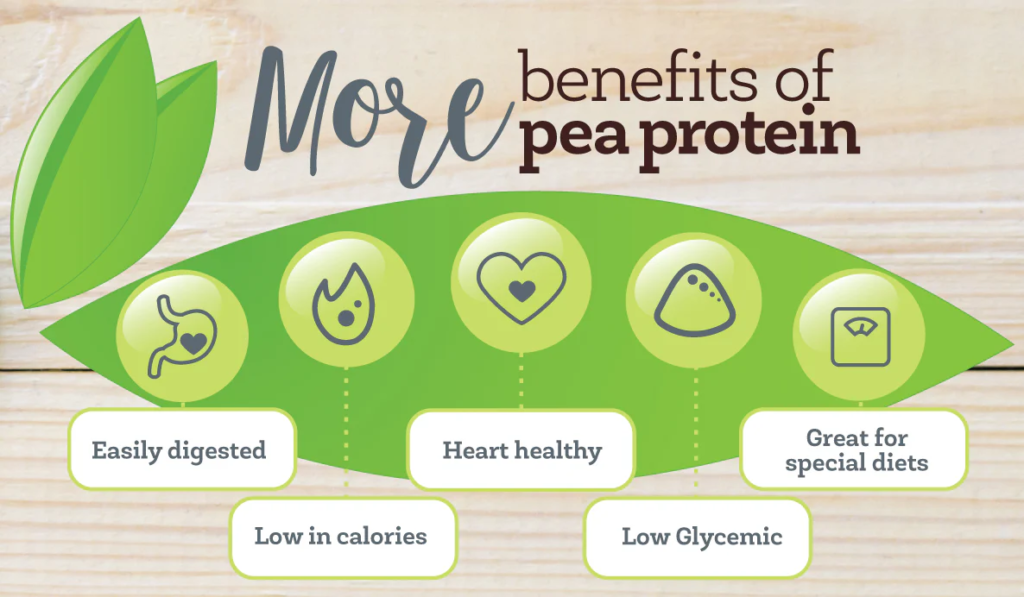
Hypoallergenic and Digestible
Unlike other common protein sources, such as dairy or soy, pea protein is hypoallergenic, making it suitable for those with food sensitivities or allergies. It’s also easy on the digestive system, which can be a significant advantage over other protein sources that may cause bloating or discomfort.
Pea Protein for Weight Management
Pea proteins are naturally low in calories and fat while being high in protein, making it a great choice for those looking to manage their weight. Studies have shown that protein can help increase satiety (the feeling of fullness), making you less likely to overeat. This makes pea protein an excellent tool for those looking to lose or maintain their weight.
Muscle Building and Recovery
If you’re into fitness, you’ll be pleased to know that pea protein is just as effective for muscle building as whey protein. Thanks to its rich BCAA content, pea protein can help stimulate muscle protein synthesis, aiding in recovery after workouts and promoting muscle growth over time.
Environmental Benefits of Pea Proteins
Sustainability of Pea Farming
Pea farming is considered highly sustainable compared to other protein sources, particularly animal-based ones. Peas require less water and fewer resources to grow, making them an eco-friendly option for those concerned about environmental impact. Moreover, pea plants contribute to soil health by naturally fixing nitrogen in the soil, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Lower Carbon Footprint Compared to Animal Proteins
The carbon footprint of plant-based proteins like pea protein is significantly lower than that of animal-based proteins like beef or dairy. By choosing pea proteins, you’re not only supporting your health but also contributing to a more sustainable food system.
Potential Downsides of Pea Proteins
Taste and Texture Considerations
While pea proteins offer many benefits, some people find its taste and texture to be less appealing than other protein powders. It can have an earthy or slightly bitter flavor, though many brands have improved their formulas by adding natural sweeteners or flavors to mask the taste.
Processing and Additives in Some Products
Not all pea protein products are created equal. Some brands heavily process their protein powders or add artificial flavors, sweeteners, or preservatives. When choosing a pea protein product, it’s important to read the label carefully and opt for minimally processed options with clean ingredients.
Nutrient Profile Gaps Compared to Animal Proteins
Though pea proteins are close to being a complete protein, it’s still slightly lacking in certain amino acids like methionine. To ensure you’re getting a full spectrum of amino acids, you might consider combining pea protein with other plant-based proteins like rice or quinoa, or simply eating a well-balanced diet.
Who Should Consider Pea Proteins?

Vegans and Vegetarians
Pea proteins are obvious choice for those following a vegan or vegetarian diet. It offers a plant-based alternative to animal-derived proteins, allowing vegans and vegetarians to meet their protein needs without compromising their ethical or dietary beliefs.
Individuals with Food Allergies or Sensitivities
If you have allergies to soy, dairy, or gluten, pea proteins could be a perfect solution. It’s naturally free from these common allergens, making it a safe and reliable option for those with specific dietary needs.
Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts
Pea proteins are particularly beneficial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts who need a high-quality protein source for muscle recovery and growth. Its amino acid profile makes it comparable to whey protein, offering a plant-based alternative without compromising on results.
How to Incorporate Pea Protein into Your Diet
Protein Shakes and Smoothies
One of the easiest ways to enjoy pea protein is by adding it to shakes or smoothies. Blend it with fruits, greens, and almond milk for a quick and nutritious post-workout drink.
Baking with Pea Protein
You can also incorporate pea protein into your baking. It works well in protein bars, muffins, pancakes, and even cookies, providing a protein boost without drastically altering the taste or texture of your treats.
Pea Proteins in Savory Dishes
Pea proteins can also be added to savory dishes like soups, stews, and veggie burgers. Its neutral flavor blends well with spices and herbs, making it a versatile ingredient in various recipes.
Conclusion: Is Pea Protein the Best Plant-Based Alternative?
Pea proteins stand out as one of the best plant-based protein alternatives due to its impressive nutritional profile, digestibility, and environmental sustainability. While it may not be perfect, particularly in terms of taste or amino acid completeness, it offers a reliable, hypoallergenic, and eco-friendly option for those seeking a plant-based lifestyle. Whether you’re an athlete, a vegan, or someone with food sensitivities, pea protein is definitely worth considering as part of your regular diet.
FAQs About Pea Protein
Is pea protein safe for people with allergies?
Yes, pea protein is hypoallergenic and free from common allergens like dairy, soy, and gluten, making it suitable for most people with food allergies.
Can I gain muscle with pea protein alone?
Yes, pea protein contains a high amount of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which are essential for muscle growth and recovery, making it comparable to whey protein for muscle-building purposes.
Does pea protein have a complete amino acid profile?
While pea protein contains all nine essential amino acids, it is slightly low in methionine. However, this can be easily compensated by combining it with other plant-based proteins like rice or quinoa.
How much pea protein should I consume daily?
The amount of pea protein you need depends on your overall protein requirements, which can vary based on age, activity level, and health goals. Typically, 20-30 grams per serving is a good starting point for most adults.
Are there any side effects of pea protein?
Pea protein is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience mild digestive discomfort, especially if they are not used to consuming high amounts of protein.



MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers