When it comes to building muscle and bouncing back after a tough workout, proteins often take center stage. For many fitness enthusiasts and athletes, getting enough protein is a top priority. But why is protein so crucial for muscle recovery and growth? Let’s dive into the details.
Table of Contents
What Is Protein?
Protein is one of the three macronutrients that our bodies need to function, alongside carbohydrates and fats. It’s made up of smaller molecules called amino acids, which are often referred to as the building blocks of life. Proteins are responsible for building and repairing tissues, including muscles, which is why they are so important for recovery and growth.
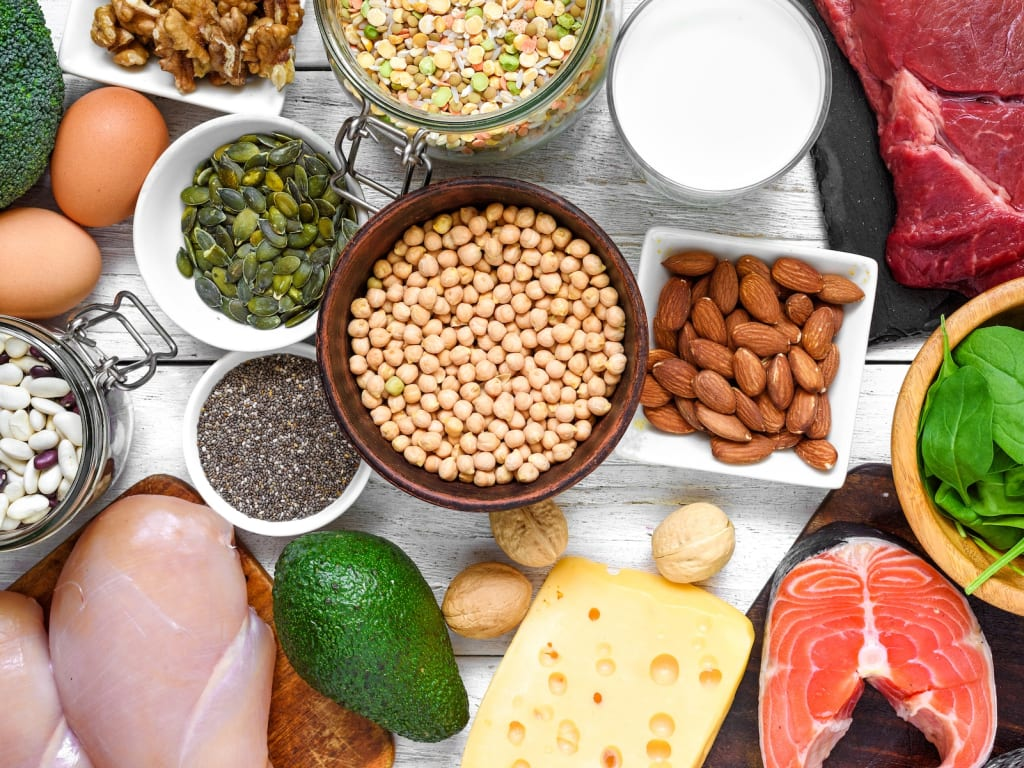

There are 20 amino acids in total, nine of which are considered essential. This means that your body can’t produce them on its own, so you need to get them from your diet.
Why Is Protein Important for Muscles?
Proteins are crucial for muscles because it plays multiple roles in building, repairing, and maintaining muscle tissue. Whether you’re trying to recover from a workout or build strength, getting enough protein is essential. Let’s explore why protein is so important for muscles.
Protein’s Role in Muscle Structure
Muscles are made up of long, fibrous proteins that are arranged in a way that allows them to contract and expand. These proteins include actin and myosin, which are responsible for muscle contractions. Without enough proteins, your muscles wouldn’t have the building blocks needed to maintain their structure and function.
Protein Synthesis and Muscle Repair
Protein synthesis is the process where your body uses amino acids from the proteins you eat to repair and build new muscle tissue. After intense exercise, such as lifting weights, your muscle fibers experience small tears. Protein is vital in repairing these tears, helping your muscles recover and grow stronger. This process is called muscle protein synthesis (MPS), and it’s directly linked to how much proteins you consume.
Overview of Proteins Breakdown and Rebuilding
When you exercise, particularly with resistance training, your muscles go through a cycle of breakdown and rebuilding. During the breakdown phase, your body breaks down muscle proteins, while during the rebuilding phase, it uses dietary proteins to repair and strengthen the muscle. This constant cycle requires a steady supply of proteins to support muscle repair and growth.
The Science Behind Muscle Recovery
To understand how protein helps with muscle recovery, it’s important to know what happens to muscles during exercise. Whether you’re running, lifting weights, or doing high-intensity training, your muscles experience micro-damage that needs to be repaired for them to grow back stronger.
How Muscles Get Damaged During Exercise
When you engage in strenuous physical activity, your muscle fibers undergo stress, leading to tiny tears. This is particularly true during resistance training, where heavy loads are placed on the muscles. This damage is a normal part of the muscle-building process, but it requires the right recovery strategies to repair the tears and build stronger muscles.
The Body’s Natural Repair Process
Once the muscle fibers are damaged, your body starts a repair process that involves delivering amino acids to the site of damage to rebuild the muscle. This is where protein plays a key role, as it supplies the necessary building blocks for repairing and strengthening the muscle tissue.
Importance of Rest and Nutrition in Recovery
While protein is crucial, recovery isn’t just about what you eat. Rest is equally important because it gives your muscles time to repair. Adequate sleep and rest days in your workout routine are vital for allowing muscle protein synthesis to occur. Without proper rest, your muscles won’t fully recover, which can lead to fatigue and even injury over time.
How Proteins Aid Muscle Recovery
Proteins are directly involved in muscle recovery by providing the essential amino acids that your body needs to repair damaged muscle fibers. Let’s take a closer look at how proteins help with muscle recovery after a workout.
Protein’s Role in Repairing Damaged Muscle Fibers
After a workout, your muscles need amino acids to rebuild. Protein-rich foods or supplements provide these amino acids, which are delivered to the damaged muscle fibers. This repair process not only restores the muscles but also strengthens them, leading to better performance in future workouts.
Accelerating Muscle Recovery After Workouts
Consuming protein after exercise helps accelerate recovery by speeding up the repair process. This can reduce soreness and fatigue, helping you get back to your workouts faster. For instance, athletes often consume protein shakes immediately after training to jumpstart the recovery process.
Examples of Specific Proteins That Promote Recovery
Casein protein: Unlike whey, casein digests slowly and provides a steady release of amino acids. This makes it useful for overnight recovery, ensuring your muscles have a continuous supply of nutrients while you sleep.
Whey protein: This is one of the most popular proteins for recovery due to its fast absorption rate. It provides a quick influx of amino acids to your muscles, making it ideal for post-workout recovery.
Protein and Muscle Growth
While protein helps repair muscles, it’s also essential for muscle growth. Building muscle, known as hypertrophy, requires an increase in muscle size, which can only happen with sufficient protein intake.
Protein’s Role in Hypertrophy (Muscle Growth)
Hypertrophy occurs when muscle protein synthesis exceeds muscle protein breakdown. Essentially, your muscles grow when they are repaired and rebuilt with extra protein. Without enough protein, your muscles won’t have the necessary resources to grow after your workouts.
The Anabolic Window and Muscle Growth
The “anabolic window” refers to the period after exercise when your body is primed to absorb nutrients, including protein. Many experts believe consuming protein within 30 to 60 minutes after a workout can optimize muscle recovery and growth, though more recent studies suggest that total protein intake throughout the day may be more important than the exact timing.
Why Protein Is Necessary for Gaining Lean Mass
Gaining lean muscle mass requires an increase in muscle tissue without excess fat. Protein is crucial because it helps build this lean muscle tissue. Even if you’re eating enough calories, without sufficient protein, your body won’t be able to convert those calories into muscle effectively.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need?
The amount of protein you need depends on several factors, including your age, weight, activity level, and fitness goals. For the average person, the recommended daily intake is about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. However, if you’re regularly engaging in strenuous exercise or strength training, your protein needs can rise to 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram.
Athletes, bodybuilders, and those looking to gain muscle mass may require even more protein to facilitate recovery and promote growth.
Best Sources of Protein for Muscle Recovery

Not all proteins are created equal, but there are plenty of great sources of both animal and plant-based protein to choose from:
- Animal-based proteins: Chicken, beef, fish, eggs, and dairy products like milk and cheese are excellent sources of complete proteins, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids.
- Plant-based proteins: Foods like lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, soy products (tofu, tempeh), and protein-rich grains can be effective alternatives. While many plant-based proteins lack one or more essential amino acids, combining different sources (like beans and rice) can provide a full profile of amino acids.
- Protein supplements: Whey, casein, and plant-based protein powders (pea, soy, rice) offer convenient, fast-digesting options that can complement whole food sources, especially when you need a quick post-workout fix.
Timing Your Protein Intake for Optimal Results
When it comes to protein timing, the “anabolic window” refers to the period immediately after a workout when your muscles are most receptive to protein. While many believe this window is crucial, studies suggest that spreading your protein intake evenly throughout the day may be just as effective.
Aim to include protein in every meal and snack to ensure your body always has a steady supply of amino acids for muscle recovery and growth.
The Role of Protein Supplements
Protein supplements are widely used to help people meet their daily protein needs, especially when trying to recover from workouts or build muscle.
When to Consider Protein Powders and Shakes
Protein powders and shakes are convenient when you need a quick source of protein, particularly after a workout. They’re also helpful if you have trouble getting enough protein from whole foods, whether due to dietary restrictions or busy schedules.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Protein Supplementation
- Benefits: Quick and easy, especially post-workout. They offer a controlled amount of protein and can be convenient for those on the go.
- Drawbacks: Supplements can be expensive and might not provide the same nutritional benefits as whole foods, which often come with vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.
Whey vs. Casein vs. Plant-Based Protein Powders
Plant-based proteins: Suitable for those who are vegan or lactose intolerant. Popular options include pea, soy, and hemp proteins, which are effective alternatives to animal-based powders.
Whey protein: Fast-absorbing and ideal for post-workout recovery.
Casein protein: Slow-digesting and great for sustained muscle recovery, particularly at night.
Protein and Other Nutrients for Muscle Recovery
While protein is essential, it’s not the only nutrient that supports muscle recovery. Other macronutrients also play a role.
Role of Carbohydrates in Muscle Recovery
Carbohydrates are important because they replenish glycogen stores that are depleted during exercise. Glycogen is the stored form of glucose, and it serves as the primary fuel for muscles during workouts. Consuming carbs with protein post-exercise helps speed up recovery by refueling these glycogen stores.
Importance of Healthy Fats Alongside Protein
Healthy fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, can help reduce inflammation after exercise. This is important for recovery, as reduced inflammation allows your muscles to heal faster and with less discomfort.
Hydration and Electrolytes
Water and electrolytes are critical for transporting nutrients to your muscles and removing waste products. Staying hydrated before, during, and after workouts ensures that your muscles can recover efficiently.
Protein for Different Types of Athletes

Different athletes have different protein requirements based on their sports and goals.
Endurance Athletes vs. Strength Athletes
- Endurance athletes (runners, cyclists, etc.) need protein to repair muscles damaged by long-duration activities. They also need carbohydrates to replenish glycogen.
- Strength athletes (bodybuilders, weightlifters) require more protein to support the demands of muscle growth and repair due to heavy lifting and resistance training.
Protein Needs for Bodybuilders
Bodybuilders, who focus on muscle hypertrophy, often consume higher amounts of protein to support muscle repair and growth. Their protein needs can be as high as 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
How Athletes in Different Sports Should Approach Protein Intake
Athletes in various sports—whether team sports like football or individual sports like swimming—should adjust their protein intake based on the intensity and frequency of their training. For most, spreading protein intake evenly across meals is the most effective strategy for supporting muscle recovery and growth.
Common Myths About Protein and Muscle Growth
One common myth is that more protein always equals more muscle. In reality, once your body has what it needs for repair and growth, the extra protein won’t magically lead to more gains. Similarly, it’s a myth that plant-based proteins are inferior; you can build muscle just as effectively with plant-based diets if planned well.
Risks of Too Little or Too Much Protein
Not getting enough protein can lead to muscle loss, weakness, and slower recovery. On the flip side, consuming too much protein can strain the kidneys, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions, and may cause digestive issues.
Conclusion
Protein plays a vital role in muscle recovery and growth. By ensuring you get enough of it in your diet, along with other essential nutrients, you can support your fitness goals and recover faster. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting, understanding the importance of protein will help you maximize your progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you build muscle without protein supplements?
Absolutely. Whole foods like chicken, beans, and quinoa can provide all the protein you need.
Is there such a thing as eating too much protein for muscle growth?
Yes, excess protein doesn’t translate to more muscle and could lead to health issues.
How soon after a workout should you eat protein?
Ideally, within 30-60 minutes, but what’s most important is total daily intake.
Are plant-based proteins as effective for muscle recovery?
Yes, as long as you consume a variety of sources to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
What’s the best time of day to consume protein for muscle growth?
Spread your intake throughout the day to ensure your muscles have a constant supply of amino acids.

MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers