Unlock the secrets of Ganglion Cysts with our comprehensive guide. From understanding their mysterious origins to exploring the latest treatment options, learn how to manage and potentially overcome these common yet perplexing cysts.
Introduction
Ganglion cysts, mysterious in origin and common in occurrence, present a unique challenge in the realm of joint and tendon conditions. Emerging from weaknesses in the joint capsule or tendon sheath, these cysts can affect anyone, leading to discomfort and mobility issues. This article delves into the causes, symptoms, and innovative treatments for Ganglion Cysts, offering hope and actionable solutions for those seeking relief.
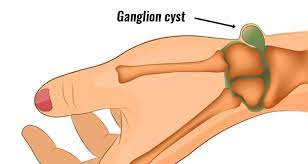
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to Ganglion Cyst Formation
Joint or Tendon Stress
Continuous or repetitive motion can heighten the risk of cysts, commonly observed in athletes or those whose occupations involve repetitive wrist and hand movements.
Trauma
An isolated injury to a joint or tendon might initiate cyst development if it results in connective tissue damage or weakness.
Mechanical Changes
Aging or previous injuries might alter joint or tendon tissue, creating an environment conducive to cyst growth.
Hormonal Factors
There’s speculation that hormonal fluctuations could impact cyst formation, though more research is needed to clarify this link.
Symptoms Associated with Ganglion Cysts
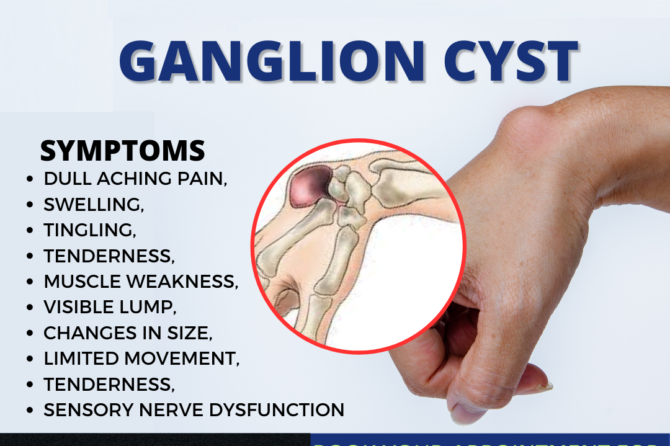
The symptoms of ganglion cysts can vary, largely depending on their size and location:
Visible Lump
A lump, varying in size, may appear over a joint or tendon. Activity can cause the lump to enlarge, while rest may reduce its size.
Discomfort or Pain
Although many cysts are painless, they can cause discomfort or pain with repetitive use of the affected joint, potentially due to pressure on surrounding tissues.
Tingling or Burning Sensation
Cysts pressing against nerves can lead to tingling, burning sensations, or numbness, particularly when located near superficial or confined nerves.
Weakness or Muscle Fatigue
Larger cysts may hinder joint movement or tendon functionality, resulting in muscle weakness or fatigue, affecting the ability to perform tasks requiring dexterity or a strong grip.
Recognizing the potential causes and symptoms of ganglion cysts is essential for early detection and management. While these cysts are typically benign, they can impact daily life and comfort for some individuals. If you notice a ganglion cyst, especially one that causes pain or affects your ability to function, seeking medical advice is recommended to explore diagnosis and treatment options.
Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
Diagnosing ganglion cysts typically involves a thorough physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history by a healthcare provider. Here’s a closer look at the diagnostic process and treatment options for ganglion cysts:
Physical Examination
The healthcare provider will examine the cyst, noting its size, shape, and mobility. A technique called transillumination, where light is passed through the cyst, may be used to determine if the cyst is solid or fluid-filled.
Pressure Application
Applying pressure to the cyst helps assess any tenderness or discomfort, providing insight into how the cyst affects the patient’s comfort and joint function.
Imaging Tests
o exclude other conditions like arthritis or tumors and to confirm the diagnosis, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be utilized. These tests offer detailed views of the cyst and its relationship to surrounding tissues.
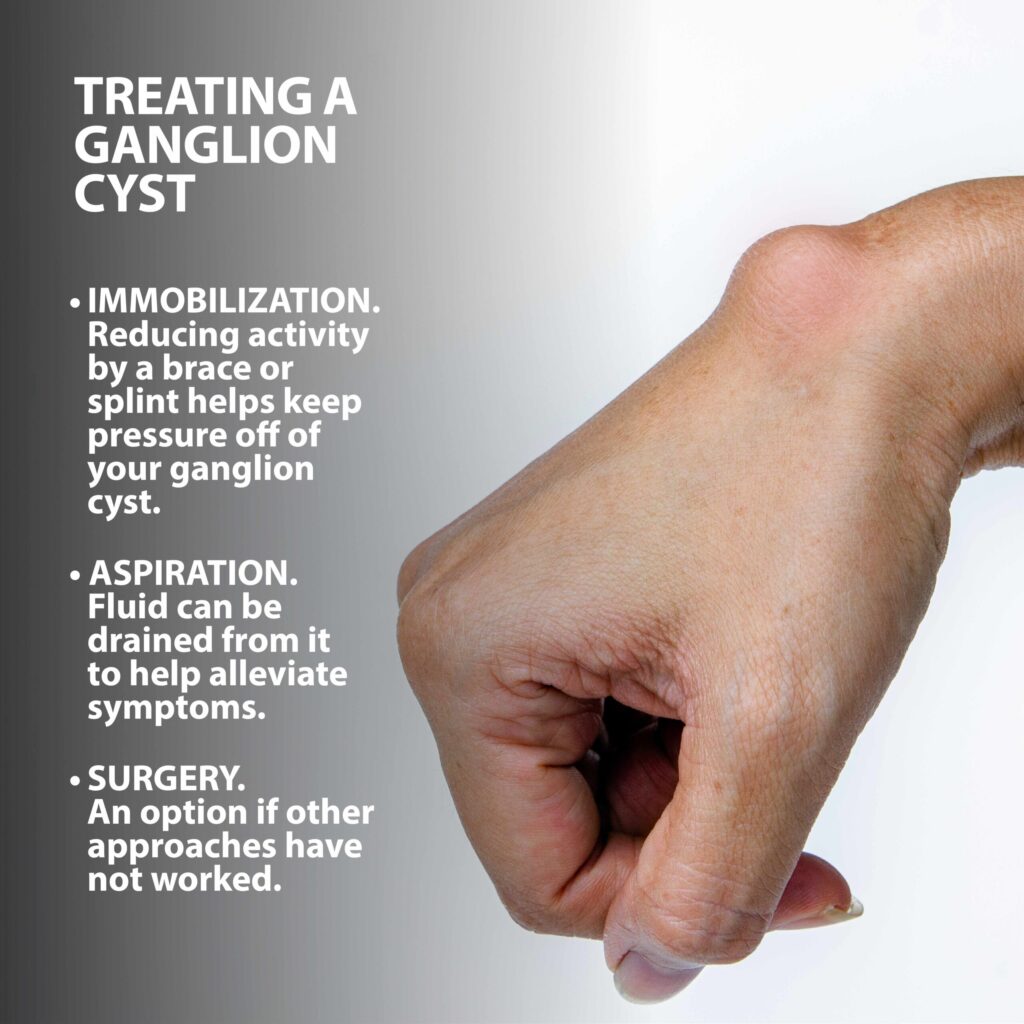
Treatment Approaches
Observation
If the cyst is not causing symptoms, it may be monitored over time, as many ganglion cysts resolve on their own without treatment.
Aspiration
For symptomatic cysts, fluid can be drained through a needle in a minimally invasive procedure. While this can offer temporary relief, there’s a possibility of the cyst recurring.
Surgery
In cases where the cyst recurs after aspiration, causes significant discomfort, or impedes joint movement, surgical removal may be considered. The surgery aims to eliminate the cyst and a portion of the joint capsule or tendon sheath to address the root cause, reducing the likelihood of recurrence but carrying typical surgical risks.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Consultation with a healthcare provider is advisable under the following circumstances:
- Pain: If the cyst causes pain or discomfort.
- Joint Movement Impairment: If the cyst’s size or location affects normal joint function.
- Symptoms of Nerve Compression: Experiencing tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness could indicate the cyst is pressing on a nerve.
- Cosmetic Concerns: Individuals may seek removal for aesthetic reasons or if the appearance of the cyst is bothersome.
Although ganglion cysts are usually benign, their management should be tailored to the individual’s symptoms and needs. Healthcare professionals can provide advice on the most appropriate treatment strategy based on each unique case.
| Arch Support |
| Arch Supports |
| Best Arch Support Insoles |
| Best Insole for Plantar Fasciitis |
| Insole for Flat Feet |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What exactly are Ganglion Cysts?
A: Ganglion Cysts are fluid-filled lumps that typically develop along the joints or tendons in the hands and wrists, though they can also appear on feet and ankles. They form due to a weakness in the joint capsule or tendon sheath, creating a bulge filled with jelly-like fluid.
Q: What causes Ganglion Cysts to form?
A: The exact cause is unknown, but factors like joint or tendon stress, trauma, mechanical changes, and possibly hormonal fluctuations are believed to contribute to their development.
Q: Are Ganglion Cysts painful?
A: While many cysts are painless, they can cause discomfort, pain, or even nerve-related symptoms such as tingling or numbness, depending on their size and location.
Q: How are Ganglion Cysts diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, possibly including transillumination, pressure application, and imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI to rule out other conditions and confirm the diagnosis.
Q: What treatment options are available for Ganglion Cysts?
A: Treatment may range from observation for asymptomatic cysts to aspiration or surgery for those causing significant discomfort or impairing joint movement.
Conclusion
Ganglion Cysts, while often benign, can impact daily life and raise numerous questions for those affected. Understanding their potential causes, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring the range of treatment options are key steps toward managing this condition effectively. With advancements in medical treatment and a deeper understanding of cyst formation, individuals have more tools at their disposal than ever before to address and overcome the challenges posed by Ganglion Cysts.

MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers