Hypothyroidism, characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, is renowned for its impact on muscle and joint discomfort. However, what’s less known is its potential to affect nerves, altering how individuals experience sensations, particularly in their peripheral tissues like the feet.
If you’re among those experiencing frequent foot pain alongside hypothyroidism, you’re not alone. While the exact extent of thyroid hormone involvement in foot pain remains unclear, it’s essential to recognize that poorly controlled thyroid function may contribute to your foot discomfort.
Table of Contents
Hypothyroidism:
Hypothyroidism is a chronic condition where the thyroid gland fails to produce adequate thyroid hormone to meet the body’s metabolic demands. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism and influencing energy usage and distribution.
Insufficient thyroid hormone levels can lead to a slowing down of bodily functions.
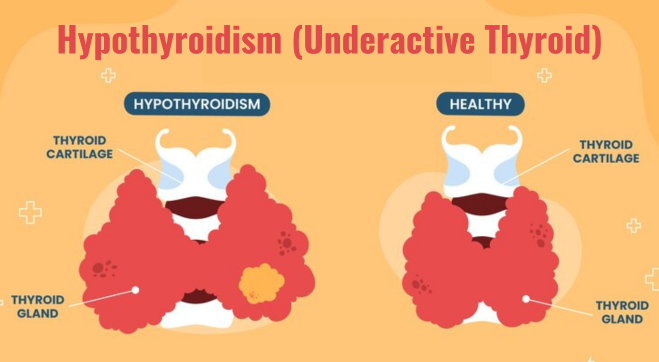
The Causes of Hypothyroidism:
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in developed countries.
- It occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and eventual damage to thyroid tissue.
- Autoimmune thyroiditis can gradually impair thyroid function, resulting in decreased production of thyroid hormones over time.
- Thyroid Surgery or Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
- People who undergo thyroid surgery to treat conditions such as thyroid cancer or nodules may develop hypothyroidism if a significant portion of the thyroid gland is removed or if its function is impaired.
- Similarly, radioactive iodine therapy, often used to treat hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), can inadvertently damage thyroid tissue, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Iodine Deficiency:
- Iodine is an essential nutrient required for the production of thyroid hormones.
- In regions where iodine intake is insufficient, such as certain parts of the world with low dietary iodine levels, hypothyroidism can occur.
- Without adequate iodine, the thyroid gland cannot produce enough thyroid hormones, resulting in hypothyroidism.
- Medications and Treatments:
- Certain medications and medical treatments can interfere with thyroid function and contribute to hypothyroidism.
- Examples include lithium, amiodarone, and some anti-thyroid medications used to treat hyperthyroidism.
- Radiation therapy, particularly when administered to the head and neck area to treat cancers, can also damage thyroid tissue and impair hormone production.
- Congenital Hypothyroidism:
- Some individuals are born with hypothyroidism, a condition known as congenital hypothyroidism.
- This can occur due to abnormalities in thyroid development during fetal growth or inherited genetic mutations affecting thyroid function.
- Early detection and treatment of congenital hypothyroidism are essential to prevent developmental delays and other complications.
Why Does Hypothyroidism Affect Muscles and Joints?
Hypothyroidism affects muscles and joints through various mechanisms related to the body’s metabolism, inflammation, and nerve function. In the case of hypothyroidism, several physiological changes can impact on muscles and joints, such as:
- Metabolic Slowdown:
- Thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate the body’s metabolism, which affects how cells use energy.
- In hypothyroidism, the decreased production of thyroid hormones slows down metabolism, resulting in reduced energy production in cells.
- This metabolic slowdown can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and sluggishness, affecting overall muscle function and performance.
- Fluid Retention and Inflammation:
- Hypothyroidism can lead to fluid retention and inflammation in the body, including the muscles and joints.
- Fluid retention can cause swelling, stiffness, and discomfort in the joints, exacerbating symptoms of conditions such as arthritis.
- Inflammation can also contribute to pain and tenderness in the muscles and joints, further impairing mobility and function.
- Muscle and Joint Stiffness:
- Reduced thyroid hormone levels can result in decreased blood flow to muscles and joints, leading to stiffness and reduced flexibility.
- This can make it challenging to perform everyday activities and increase the risk of injury.
- Muscle stiffness may also contribute to joint pain and discomfort, particularly in weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips.
- Nerve Dysfunction:
- Thyroid hormones play a role in maintaining the health and function of the nervous system, including peripheral nerves that transmit signals to and from the muscles and joints.
- In hypothyroidism, nerve function may be impaired due to reduced thyroid hormone levels, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and neuropathic pain in the muscles and joints.
- Autoimmune Inflammation:
- In cases where hypothyroidism is caused by autoimmune thyroiditis, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, autoimmune inflammation may contribute to muscle and joint problems.
- Autoimmune diseases can cause the immune system to attack healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage in the muscles and joints.
Managing Foot Pain Associated with Hypothyroidism:
Living with hypothyroidism can be challenging, especially when foot pain becomes a daily struggle. However, effective management involves a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying thyroid dysfunction while also implementing strategies to alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
Managing foot pain associated with hypothyroidism involves a multifaceted approach:
1. Diagnosis: Seek Thyroid Function Testing
If you suspect hypothyroidism may be contributing to your foot pain, seeking a thyroid function test is essential.
This test evaluates your thyroid hormone levels and can detect any autoimmune processes affecting thyroid function. Proper diagnosis is the first step toward effective management.
2. Medication: Correcting Thyroid Hormone Levels
One of the cornerstones of managing hypothyroidism is correcting low thyroid hormone levels with medication such as levothyroxine.
Finding the right dosage may take time and requires close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
However, it’s essential for alleviating associated symptoms, including foot pain.
3. Weight Management: Supporting Foot Health
Weight management plays a crucial role in reducing foot pain associated with hypothyroidism.
Excess weight can exacerbate discomfort and strain on the feet.
Therefore, adopting healthy lifestyle habits and engaging in regular physical activity is important.
However, it’s crucial to choose low-impact exercises like swimming or stationary biking to avoid exacerbating foot pain.
4. Pain Relief: Over-the-Counter Medications
In addition to managing thyroid hormone levels and maintaining a healthy weight, over-the-counter medications can provide temporary relief from foot pain.
Ibuprofen or acetaminophen are commonly used to alleviate discomfort.
It’s important to take these medications as directed, preferably before engaging in physical activity to maximize their effectiveness.
5. Lifestyle Modifications: Supporting Foot Health
In addition to medication and pain relief, making lifestyle modifications can further support foot health.
This includes wearing supportive footwear with adequate cushioning and arch support, especially if you spend long hours on your feet.
Additionally, incorporating foot exercises and stretches into your daily routine can help improve flexibility and strength, reducing the risk of injury and discomfort.

Foot pain in hypothyroidism is complex and multifaceted, involving various factors ranging from autoimmune processes to associated conditions like weight gain and neuropathy.
By understanding these complexities and implementing a comprehensive management plan involving medication, lifestyle modifications, and pain relief strategies, anyone can effectively manage foot pain and improve their overall quality of life.
Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for personalized treatment and optimal outcomes.


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Pea Proteins: The Best Plant-Based Protein Alternative?
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments