Athlete’s foot, medically termed tinea pedis, stands as one of the most prevalent fungal infections affecting the feet.
This condition, marked by symptoms such as persistent itching, burning sensations, and the development of cracked skin—particularly between the toes—can induce discomfort and inconvenience if not duly addressed. Recognizing its signs and knowing how to effectively manage and prevent its recurrence are crucial steps toward maintaining foot health and overall well-being.
Table of Contents
Symptoms of Athlete’s Foot:
The symptoms of an athlete’s foot manifest along a spectrum of discomfort and can vary in intensity and presentation from person to person.
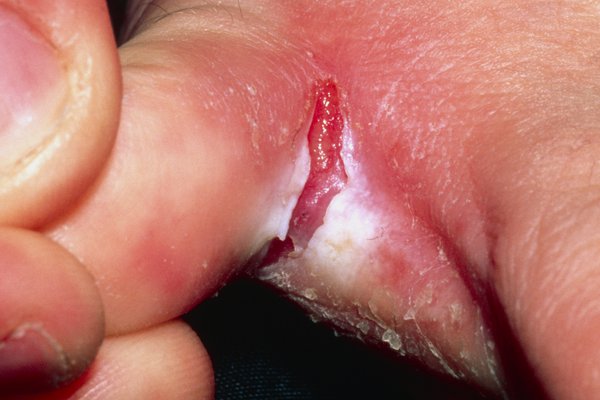
Common indications include:
- Intense Itching: The athlete’s foot typically initiates with an insistent itching sensation, notably pronounced between the toes where moisture tends to accumulate.
- Burning Sensation: Affected areas often experience a burning or stinging sensation, further exacerbating the discomfort.
- Redness and Inflammation: The infected skin may appear red, swollen, and inflamed, signaling the body’s immune response to the fungal invasion.
- Peeling or Cracked Skin: Dry, flaky, or cracked skin, especially in the interdigital spaces, is a hallmark feature of an athlete’s foot.
- Formation of Blisters: In more severe cases, the infection may lead to the formation of small blisters, adding to the discomfort and hindering mobility.
- Thickened, Discolored Toenails: Advanced stages of athlete’s foot may involve the fungal infection spreading to the toenails, resulting in thickened, discolored, and brittle nails.
- Foul Odor: Bacterial and fungal proliferation on the skin can lead to the emission of a characteristic foul odor, particularly pronounced in enclosed footwear.
Managing and Preventing Athlete’s Foot:
Effective management and prevention strategies play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of an athlete’s foot on daily life and overall foot health. Incorporating the following practices into one’s routine can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the likelihood of recurrence:
Maintain Cleanliness and Dryness:
- Daily washing of the feet with soap and water, coupled with thorough drying—especially between the toes—can help eliminate fungal spores and prevent moisture buildup, which serves as an optimal environment for fungal growth.
Choose Breathable Footwear:
- Opting for shoes crafted from breathable materials, such as leather or mesh, facilitates adequate air circulation, thereby minimizing sweat accumulation and reducing the risk of fungal proliferation.
Regularly Change Socks:
- Changing socks daily, particularly if one’s feet tend to perspire profusely, helps maintain dryness and prevents the buildup of moisture, which is conducive to fungal growth.
Use Antifungal Products:
- Over-the-counter antifungal powders or sprays can be applied to the feet and inside shoes to inhibit fungal growth and maintain a dry environment.
- Rotating between different pairs of shoes allows for proper airing and drying.
Avoid Barefoot Walking in Public Areas:
- Utilizing shower shoes or sandals in communal spaces such as locker rooms and swimming pools reduces direct contact with potentially contaminated surfaces, thereby minimizing the risk of infection transmission.
Maintain Proper Foot Hygiene:
- Regular inspection of the feet for any signs of infection, coupled with prompt treatment of symptoms, is essential in preventing the progression of the athlete’s foot and averting complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Foot Care:
While self-care measures suffice for many cases of athlete’s foot, prompt medical attention is warranted under certain circumstances:
- Persistence of symptoms despite over-the-counter treatments.
- Experiencing significant discomfort or spreading infection.
- Presence of underlying health conditions such as diabetes or compromised immune function.
Preparing for Medical Appointment:
Ahead of a medical consultation, individuals should:
- Compile a detailed account of symptoms, including onset and severity.
- List current medications and supplements.
- Bring along footwear for examination, if feasible.
- Provide relevant medical history and prepare questions for the healthcare provider.
Medical Treatment:
Medical interventions for athlete’s foot may include:
- Prescription antifungal medications, tailored to the severity of the infection.
- Topical steroids to alleviate inflammation and itching.
- Antibiotics if secondary bacterial infections arise.
- Foot soaks with antifungal agents to aid in symptom relief and healing.
Furthermore, lifestyle and hygiene recommendations are typically emphasized to prevent recurrence and promote overall foot health.
Choosing Proper Insoles for Athlete’s Foot:
In selecting insoles conducive to managing athlete’s foot symptoms, several key considerations come into play:
- Incorporation of antimicrobial properties to curb fungal and bacterial growth.
- Utilization of moisture-wicking materials to maintain dryness.
- Integration of breathable design elements to facilitate air circulation.
- Provision of adequate cushioning and support for enhanced comfort.
- Implementation of odor control features to mitigate unpleasant smells.
- Adoption of a removable and washable design for ease of maintenance.
- Ensuring proper fit and compatibility with various types of footwear.
Regular replacement of insoles is advisable to uphold their effectiveness and support foot health over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Athlete’s Foot:
- What is an athlete’s foot?
- Ans: Athlete’s foot, medically known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It is caused by various types of fungi and typically manifests as itching, burning, and cracked skin, particularly between the toes.
- What are the common symptoms of an athlete’s foot?
- Ans: Common symptoms include intense itching, burning sensations, redness, inflammation, peeling or cracked skin, formation of blisters, thickened or discolored toenails, and sometimes, a foul odor.
- How is the athlete’s foot transmitted?
- Ans: Athlete’s foot is often spread through direct contact with contaminated surfaces or by coming into contact with the fungi responsible for the infection. Walking barefoot in damp public areas like locker rooms, swimming pools, and communal showers increases the risk of transmission.
- Can the athlete’s foot spread to other parts of the body?
- Ans: Yes, an athlete’s foot can spread to other parts of the body, including the hands and groin. This can occur through scratching or touching the infected area and then touching other parts of the body.
- How can an athlete’s foot be prevented?
- Ans: Preventive measures include maintaining good foot hygiene by washing feet regularly, keeping them dry, wearing breathable footwear, changing socks daily, avoiding walking barefoot in public areas, and refraining from sharing personal items like towels and shoes.
- What are the treatment options for an athlete’s foot?
- Ans: Treatment typically involves over-the-counter antifungal medications such as creams, sprays, or powders. In more severe cases, prescription-strength antifungal medications may be necessary. Topical steroids may also be prescribed to reduce inflammation, and antibiotics might be needed if a bacterial infection develops.
- When should I see a doctor for an athlete’s foot?
- Ans: It is advisable to seek medical attention if over-the-counter treatments fail to provide relief, if symptoms worsen or persist despite self-care measures, if there is significant discomfort, or if there are signs of a secondary bacterial infection. Individuals with underlying health conditions like diabetes or compromised immune systems should also consult a doctor promptly.
- Can an athlete’s foot recur after treatment?
- Ans: An athlete’s foot can recur, especially if preventive measures are not followed diligently. To reduce the risk of recurrence, it is essential to continue practicing good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and avoiding known risk factors.
- Are there any home remedies for athlete’s foot?
- Ans: Some people find relief from athlete’s foot symptoms by soaking their feet in a mixture of vinegar and water or applying tea tree oil or garlic extract to the affected area. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before trying home remedies to ensure they are safe and effective.
- Can an athlete’s foot lead to complications?
- Ans: While the athlete’s foot itself is not usually serious, complications can arise if the infection spreads to other parts of the body or if secondary bacterial infections occur. Individuals with diabetes or compromised immune systems are at higher risk of developing complications and should seek medical attention promptly if they suspect an infection.
Conclusion:
Athlete’s foot, though common, necessitates diligent management to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. By adhering to proper foot hygiene practices, wearing appropriate footwear, and seeking timely medical intervention when needed, you can effectively combat this fungal infection and safeguard foot health. Prevention remains paramount, underscoring the importance of proactive measures in maintaining fungus-free feet and ensuring overall well-being.


MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers