Whey proteins have become a staple in the fitness world and beyond, known for its remarkable ability to support muscle growth, aid in weight loss, and improve overall health. Whether you’re an athlete looking to build strength, someone trying to shed a few pounds, or just interested in boosting your daily protein intake, whey protein has something to offer. But what exactly is whey protein, and how can it fit into your health routine? Let’s explore its benefits, uses, and potential side effects.
Table of Contents
What Are Whey Proteins?
Whey protein is a high-quality protein derived from milk during the cheese-making process. When milk is curdled, whey is the liquid byproduct left behind. This liquid is then processed and dried into powdered whey protein, which can be used as a dietary supplement.

There are three main types of whey protein:
- Whey Proteins Concentrate (WPC): Contains low levels of fat and carbohydrates, with a protein content ranging from 30% to 90%.
- Whey Proteins Isolate (WPI): Almost entirely protein, with minimal fat or lactose, making it a preferred option for those who are lactose intolerant.
- Whey Proteins Hydrolysate (WPH): Predigested for easier absorption and faster digestion, ideal for people with sensitive stomachs.
Nutritional Composition of Whey Protein
Whey protein is packed with essential nutrients, including:
- Protein: A high concentration of protein (around 20-25 grams per scoop).
- Amino Acids: Contains all nine essential amino acids, including branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) like leucine, which is crucial for muscle repair.
- Low Carbs and Fats: Most whey proteins have minimal carbohydrates and fats, especially isolates, making them a great option for those following a lean diet.
Health Benefits of Whey Proteins
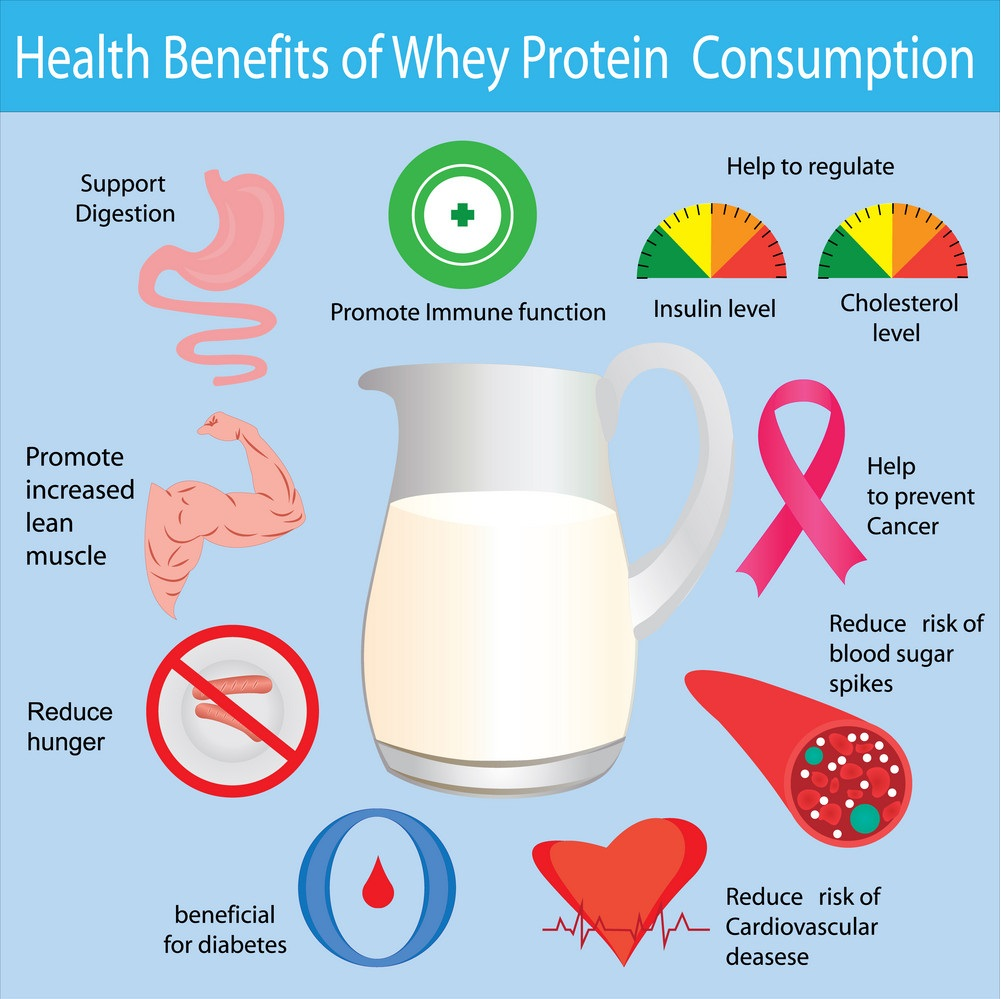
Supports Muscle Growth and Repair
Whey protein is rich in leucine, an amino acid that plays a key role in muscle protein synthesis, the process that repairs muscle fibers after intense exercise. This makes whey protein an excellent supplement for athletes and bodybuilders, aiding in muscle recovery and growth.
Weight Loss and Fat Burning
Whey protein helps control appetite, keeping you full for longer periods. By consuming whey protein as a meal replacement or snack, you can reduce overall calorie intake. Additionally, it boosts metabolism, aiding in fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass.
Improves Athletic Performance
Athletes can benefit from whey protein not only for muscle growth but also for improved endurance. Studies show that whey protein may reduce muscle soreness, allowing for quicker recovery and better overall performance.
Supports Immune Health
Whey protein contains bioactive compounds like immunoglobulins that can enhance immune function. It also supports the body’s ability to fight off infections, making it beneficial for overall health.
Improves Skin and Hair Health
Whey protein contains nutrients that promote collagen production, which improves skin elasticity and reduces signs of aging. Additionally, it strengthens hair by providing the necessary building blocks for keratin production.
Uses of Whey Proteins
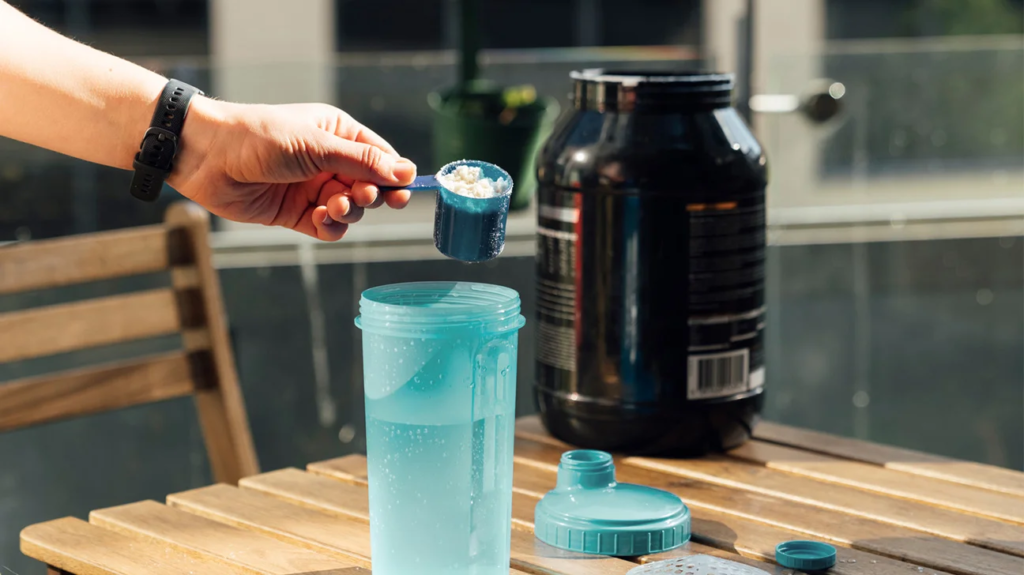

For Bodybuilding and Strength Training
For those focused on muscle gain, whey proteins are ideal both before and after workouts. It helps repair and build muscle fibers, making it easier to achieve strength and size gains.
For Weight Loss and Management
When trying to lose weight, incorporating whey proteins into your diet can help by curbing hunger and reducing overall calorie intake. Many people use it as part of meal replacement shakes or as a quick, high-protein snack.
For General Health
Whey protein isn’t just for athletes. It’s also useful for older adults who want to maintain muscle mass or anyone who struggles to meet their daily protein needs through diet alone.
How to Take Whey Protein

Best Time to Take Whey Proteins
The best time to consume whey proteins depend on your goals. Post-workout shakes help with muscle recovery, while taking it in the morning or as a snack can keep you feeling full and satisfied throughout the day.
How Much Whey Proteins to Consume
The recommended intake varies, but most people aiming to build muscle consume 1-2 scoops per day, typically delivering 20-40 grams of protein. If you’re just supplementing your diet, one scoop is usually enough.
Mixing Whey Proteins
Whey proteins are highly versatile. You can mix it with water, milk, or blend it into smoothies. There are also various flavors available to suit different tastes.
Who Should Use Whey Proteins?
Whey proteins are suitable for a wide range of people, including:
- Athletes and Bodybuilders
- People Looking to Lose Weight
- Older Adults for Muscle Maintenance
- Individuals with Dietary Restrictions (e.g., vegetarians who need more protein)
Possible Side Effects of Whey Protein

Digestive Issues
Some people experience bloating, gas, or discomfort when consuming whey proteins, especially if they are lactose intolerant.
Kidney Concerns
While moderate whey protein consumption is generally safe, excessive intake might strain the kidneys, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney issues.
Allergic Reactions
People with dairy allergies should avoid whey proteins as it can cause allergic reactions.
How to Minimize Side Effects
To reduce potential side effects, consider choosing the right type of whey proteins. For instance, whey isolate has less lactose, making it a better choice for those with lactose intolerance. Consuming whey proteins in moderation and pairing it with fiber-rich foods can also help improve digestion.
Whey Proteins vs. Other Protein Supplements
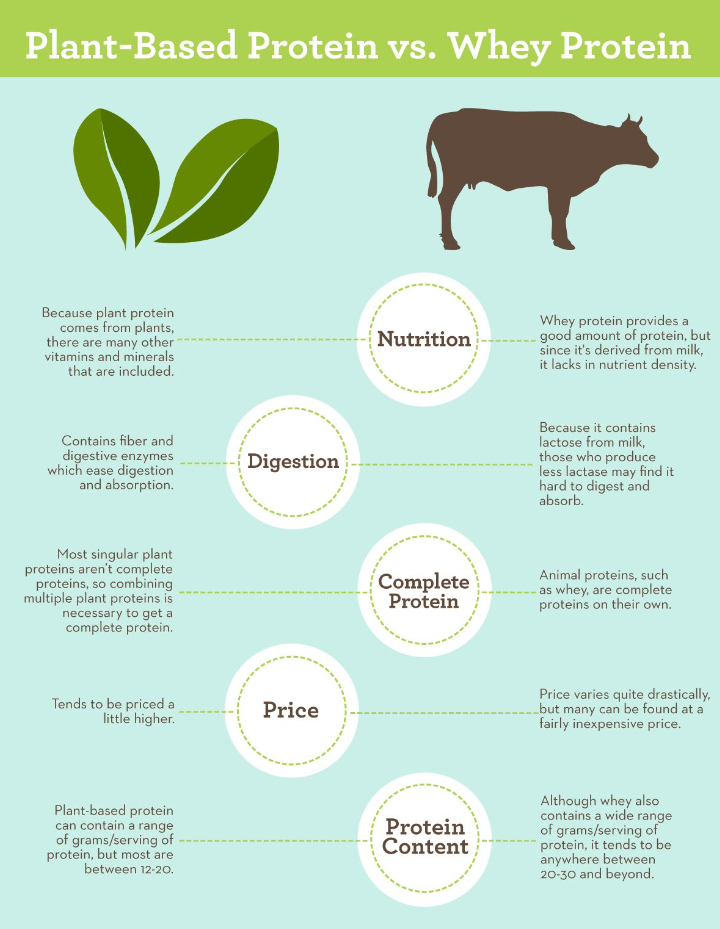
Whey vs. Casein
While whey is fast-absorbing, casein digests slowly, making it ideal for nighttime use.
Whey vs. Plant-Based Proteins
Whey is a complete protein, whereas some plant-based proteins may lack one or more essential amino acids.
Whey vs. Collagen
Whey supports muscle growth, while collagen is primarily for skin, joint, and bone health.
Choosing the Right Whey Protein
When selecting whey proteins, always check the ingredient list for additives and artificial sweeteners. Choose a product that aligns with your fitness goals—whey concentrate for general use, whey isolate for cutting, and hydrolysate for easy digestion.
Is Whey Protein Safe?
For most people, whey protein is perfectly safe when consumed in moderation. Many concerns, such as kidney damage or osteoporosis, are myths with no strong scientific backing when used appropriately.
Conclusion
Whey protein offers an impressive range of benefits, from supporting muscle growth to aiding in weight loss and improving immune function. However, like any supplement, it’s essential to use it wisely and in moderation. Whether you’re an athlete, on a weight loss journey, or simply want to add more protein to your diet, whey protein is a convenient and effective option.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is whey protein safe for long-term use?
Yes, when consumed in moderation, whey protein is safe for long-term use.
Can I take whey protein without working out?
Yes, you can still benefit from whey protein to meet daily protein requirements, even without exercising.
How does whey protein help with weight loss?
Whey protein reduces appetite, helps maintain muscle mass, and boosts metabolism, aiding in weight loss.
What’s the difference between whey protein concentrate and isolate?
Whey isolate contains more protein and less lactose and fat compared to whey concentrate.
Can children take whey protein?
While whey protein is generally safe, it’s best to consult a doctor before giving it to children.









Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you really know what you’re talking about! Bookmarked.