Introduction to Collagen Protein
Collagen protein is one of the most abundant proteins in the human body, playing a critical role in maintaining structural integrity. But what exactly is collagen, and why is it so vital to our overall health?
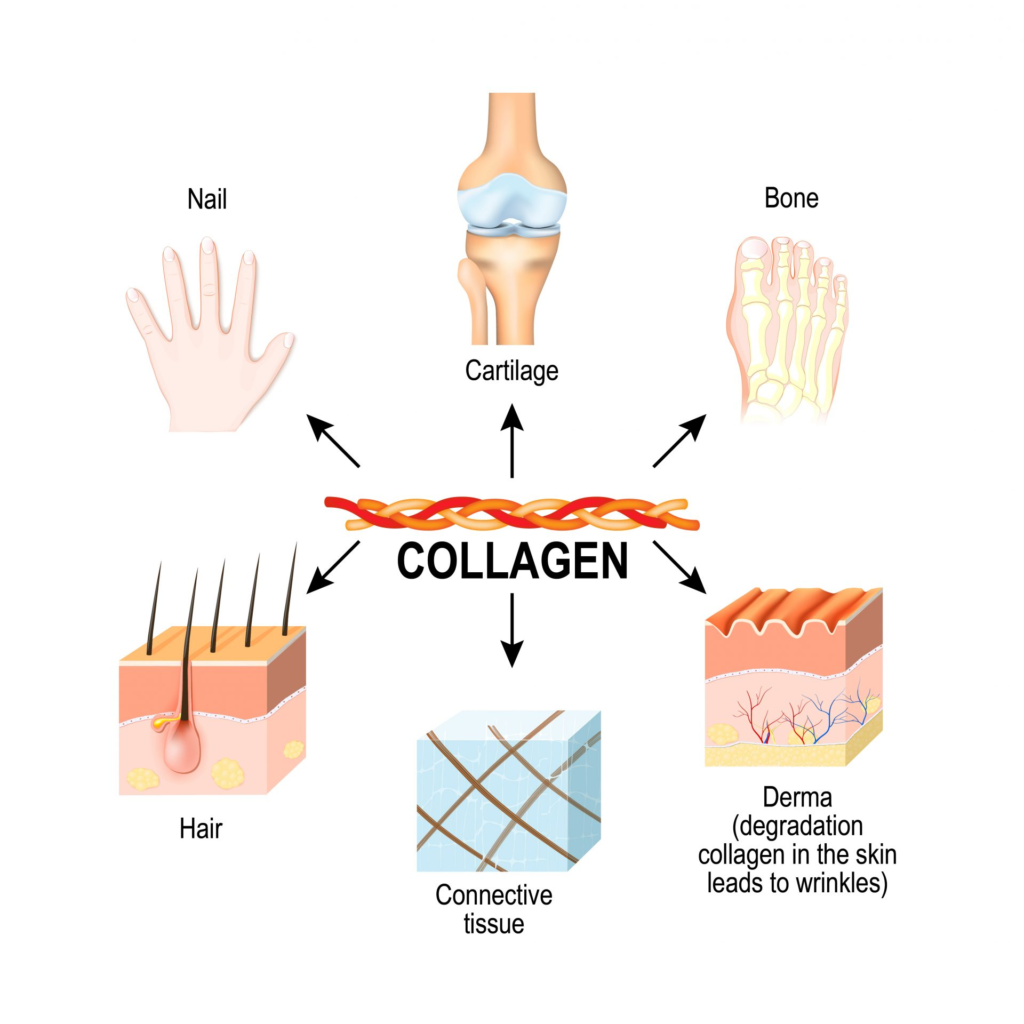
Table of Contents
What is collagen?
Collagen is a structural protein composed mainly of amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids form long chains that give collagen its characteristic toughness and flexibility. Found in skin, bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, collagen acts like the glue that holds our bodies together.
Role of collagen in the body
Beyond its structural role, collagen supports cellular processes such as tissue repair, immune responses, and skin regeneration. As we age, natural collagen production declines, leading to wrinkles, joint discomfort, and other signs of aging. This is where collagen supplementation comes in to fill the gap, offering far-reaching benefits beyond just muscle health.
How Collagen Differs from Other Proteins
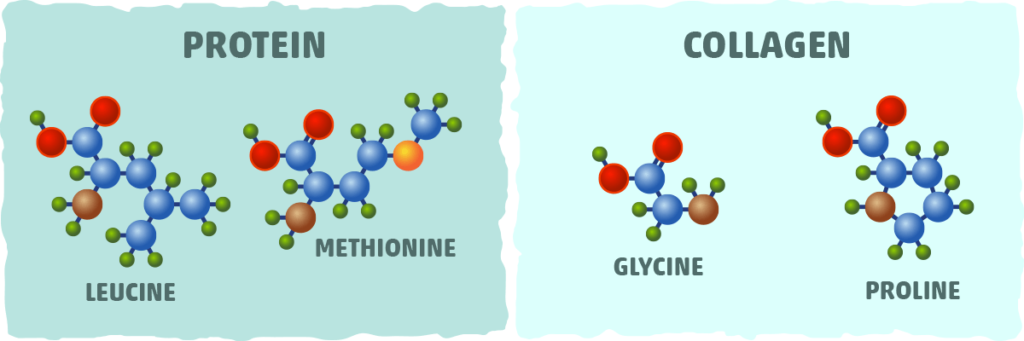
Unique amino acid profile of collagen
Unlike whey or plant-based proteins, collagen is rich in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids are essential for building connective tissues, unlike the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) that promote muscle protein synthesis. This makes collagen uniquely suited for non-muscle-related functions.
Sourcing collagen protein supplements
Collagen supplements are typically derived from animal sources such as bovine hides, chicken cartilage, or marine fish. They are hydrolyzed into peptides for better absorption and are available in powders, capsules, and liquids.
Collagen and Skin Health

Promotes skin elasticity and hydration
Collagen is a powerhouse for skin health, as it strengthens the skin barrier and retains moisture. Studies show that collagen supplements improve elasticity, reducing sagging and dryness.
Reduces visible signs of aging
Wrinkles and fine lines are often attributed to the loss of collagen in the skin. Regular supplementation can minimize these signs, leading to a smoother, more youthful appearance.
Joint and Bone Support
Benefits for cartilage and joint function
Collagen supports cartilage repair, making it a go-to supplement for those with joint issues like arthritis. It replenishes the proteins lost in cartilage, reducing pain and stiffness.
Collagen and bone density improvement
As we age, bone density decreases, leading to conditions like osteoporosis. Collagen supplementation promotes bone health by stimulating bone-forming cells and improving mineral density.
Hair and Nail Strengthening
Role of collagen in hair growth
Collagen provides amino acids essential for keratin production, the protein that strengthens hair. Regular intake can lead to thicker, shinier hair and may slow hair thinning.
Benefits for nail durability and health
Brittle nails are often a sign of protein deficiencies. Collagen helps improve nail strength and reduces splitting or breakage.
Gut Health and Digestion
Repairing the gut lining with collagen
Collagen’s amino acids, particularly glycine, are beneficial for repairing the gut lining. This is crucial for conditions like leaky gut syndrome, where the intestinal wall is compromised.
Support for digestive health and nutrient absorption
A healthy gut absorbs nutrients more efficiently, and collagen helps maintain digestive balance. This can lead to better energy levels and overall wellness.
Enhancing Athletic Recovery and Performance
Muscle recovery benefits of collagen
Collagen protein is not just about building skin or hair—it plays a significant role in athletic recovery. Its amino acid composition aids in the repair of connective tissues and reduces post-workout inflammation. Glycine and proline in collagen help rebuild muscle fibers damaged during intense training, speeding up recovery times.
Moreover, collagen is a key player in tendon and ligament health. Athletes often stress these tissues, and collagen supplementation can enhance their elasticity and strength, allowing for faster recovery and improved performance. Studies even suggest that collagen supplementation can reduce exercise-induced joint pain, making it an invaluable addition to an athlete’s regimen.
Injury prevention and repair
Collagen provides structural integrity to ligaments, tendons, and cartilage, lowering the risk of injuries. For those recovering from sports injuries, collagen can be a game-changer. It supports tissue regeneration and speeds up wound healing, especially in tendons and ligaments, which are notoriously slow to heal naturally.
Cardiovascular Health
Role of collagen in arterial elasticity
Your cardiovascular system relies on collagen to maintain the structural integrity of your arteries. Collagen contributes to arterial elasticity, ensuring that blood flows smoothly and efficiently. Without enough collagen, arteries can become stiff and prone to damage, increasing the risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular issues.
Preventing heart-related issues
Collagen’s benefits extend to reducing the risk of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by plaque build-up in arteries. It also strengthens the heart’s connective tissues, potentially lowering the risk of heart disease. Supplementing with collagen may support long-term cardiovascular health by maintaining flexible, healthy blood vessels.
Collagen for Weight Management

Boosts satiety and curbs hunger
Collagen protein helps with weight management by keeping hunger pangs at bay. Its high glycine content supports serotonin production, a hormone linked to feelings of fullness and satisfaction. A scoop of collagen in your morning coffee or smoothie can reduce mid-morning snack cravings.
Role in metabolic health
Collagen is also beneficial for maintaining muscle mass during weight loss. It supports lean muscle tissue, which is critical for a healthy metabolism. Glycine enhances metabolic functions by assisting in energy production, helping you burn calories more efficiently.
Immune System Support
Collagen and inflammation control
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many health issues, and collagen’s anti-inflammatory properties can help. Glycine and proline reduce inflammatory markers, improving overall immune function and promoting faster recovery from illnesses or injuries.
Strengthening immune responses
Collagen supports the gut, where a large portion of your immune system resides. By strengthening the gut lining, collagen prevents harmful substances from entering the bloodstream, thereby enhancing your immune system’s effectiveness.
Practical Tips for Collagen Supplementation

Best sources of collagen protein
There are various types of collagen available, sourced from bovine, marine, or poultry. Marine collagen is highly bioavailable, while bovine collagen is rich in type I and III collagen, beneficial for skin and joints. Choose a supplement free of additives and sourced from high-quality, grass-fed, or wild-caught animals.
How to incorporate collagen into your diet
Adding collagen to your routine is simple. Mix it into coffee, smoothies, or oatmeal for a morning boost. It’s tasteless and dissolves easily, making it versatile for cooking or baking. Bone broth is another natural source of collagen, ideal for soups or as a standalone drink.
Myths and Misconceptions About Collagen Protein
Is collagen just a beauty trend?
While collagen has gained attention for its beauty benefits, it’s far from a fleeting trend. Its effects on joint, bone, and cardiovascular health make it a well-rounded supplement backed by science, not just a marketing gimmick.
Addressing common concerns and doubts
Some people believe collagen supplements don’t work because they’re broken down in the digestive system. However, hydrolyzed collagen peptides are designed for optimal absorption and have been proven to increase collagen levels in the body.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Who should avoid collagen supplements?
Although collagen is generally safe, individuals with allergies to the source (e.g., fish or beef) should avoid certain types. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before starting supplementation.
Tips for safe and effective use
Start with a small dose and monitor for any adverse reactions, such as digestive upset. Stick to reputable brands and avoid supplements with unnecessary additives. Consistency is key—take collagen daily for optimal results.
Conclusion
Collagen protein is a powerhouse nutrient that goes far beyond muscle health. From enhancing skin elasticity to supporting joint function, improving gut health, and boosting athletic performance, its benefits are diverse and scientifically backed. Incorporating collagen into your daily routine is a step toward a healthier, more vibrant life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can collagen help with weight loss?
Yes, collagen boosts satiety, reducing hunger and supporting muscle maintenance, which can aid in weight management.
What is the best time to take collagen?
You can take collagen anytime, but consuming it in the morning or post-workout enhances absorption and benefits.
How long before collagen shows results?
Most people see improvements in skin, hair, and joint health within 4–8 weeks of consistent use.
Is collagen safe for long-term use?
Yes, collagen is safe for long-term use for most people, provided you choose high-quality supplements.
Are all collagen supplements the same?
No, they vary in type, source, and quality. Choose hydrolyzed collagen peptides for better absorption and ensure the product is from a trusted brand.



MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Pea Proteins: The Best Plant-Based Protein Alternative?
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Moringa Powder / Moringa Supplement
Green Superfood: The Ultimate Guide to Moringa Leaf Powder
Moringa Powder
Supercharge Your Diet: The Incredible Impact of Moringa Leaf Powder
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Shin Splints / Foot Health / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Overcoming Shin Splints – Discover Healing Strategies