Unlock the secrets to overcoming Sesamoiditis with our comprehensive guide. Learn about innovative relief strategies, prevention tips, and the path to recovery for enduring foot health.

Introduction
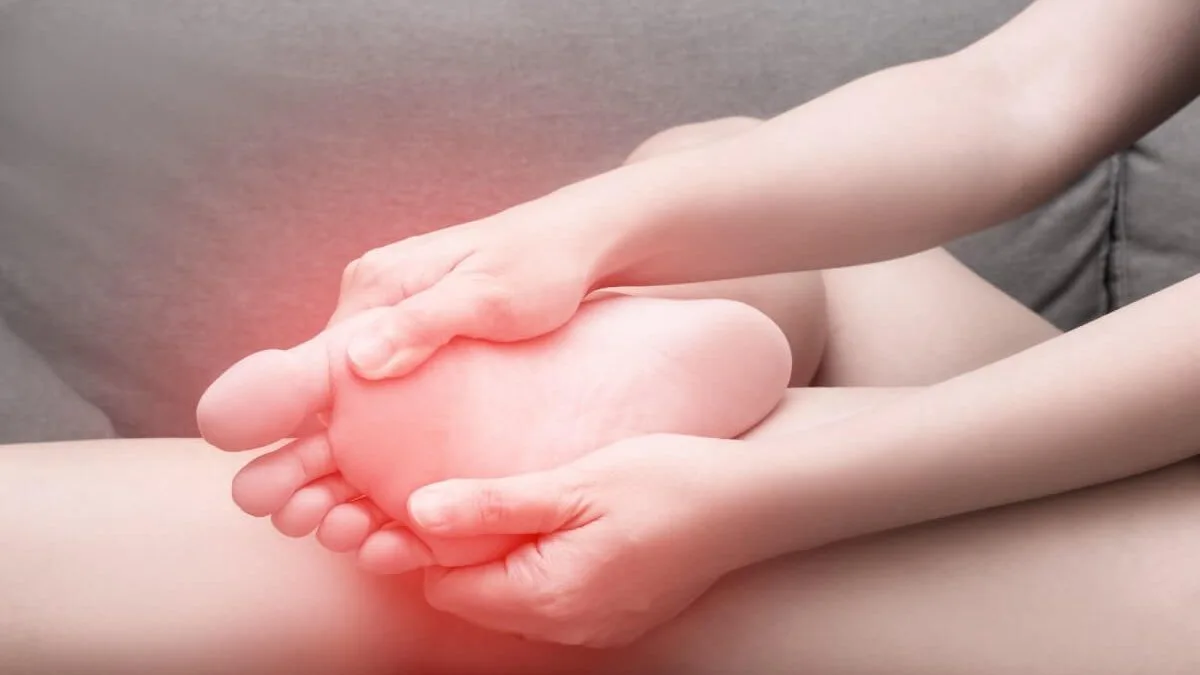
Sesamoiditis, a condition marked by pain and inflammation under the big toe, can significantly hinder daily activities like walking, running, or standing. Stemming from issues with the sesamoid bones, this ailment requires keen awareness and timely intervention. Our guide delves into the causes, symptoms, and effective treatment strategies for Sesamoiditis, offering a beacon of hope for those seeking relief and a return to comfort.
Table of Contents
What is Sesamoiditis?
Sesamoiditis is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the area under the big toe, significantly affecting one’s ability to walk, run, or even stand comfortably. This discomfort stems from issues with the sesamoid bones—two small, pea-shaped bones located beneath the joint of the big toe in the forefoot. These bones are nestled within tendons and play a pivotal role in foot mechanics, acting as a pivot point for tendons to facilitate foot movement. Due to their critical location, they are susceptible to inflammation and injuries, leading to sesamoiditis.
Key Causes of Sesamoiditis
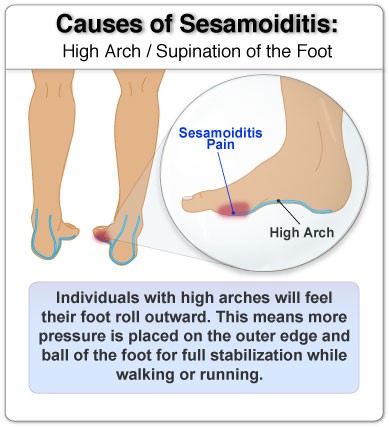
Sesamoiditis typically results from repetitive actions that place undue stress on the forefoot, particularly:
| High-Impact Sports: Engaging in sports like running, basketball, and soccer, which demand extensive footwork, can exert excessive pressure on the sesamoid bones. |
| Dance: Ballet dancers are especially at risk due to constant forefoot pressure from dancing on their toes. |
| Occupational Risks: Professions that involve prolonged periods of standing or walking can also lead to sesamoiditis. |
Risk Factors for Sesamoiditis
Certain conditions and lifestyle choices can increase the likelihood of encountering sesamoiditis:
Improper Footwear: Shoes lacking adequate support or with high heels can disrupt foot alignment and pressure distribution, raising the risk. Tight toe boxes that compress the toes may also lead to sesamoiditis.
Foot Structure: Individuals with high arches may experience increased force on the ball of the foot, predisposing them to sesamoiditis. Similarly, those with flat feet or other foot structural issues might undergo altered mechanics, placing extra stress on the sesamoid bones.
Pre-existing Foot Conditions: Conditions that affect weight distribution across the foot, such as bunions or hammertoes, can heighten the risk of developing sesamoiditis.
Key Symptoms to Be Aware Of
Recognizing the early signs of sesamoiditis is essential for timely and effective intervention. This condition, characterized by discomfort beneath the big toe, can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. Below, we outline the primary symptoms to monitor and the steps involved in diagnosing sesamoiditis, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this foot ailment.
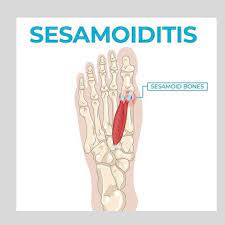
Persistent Pain Under the Big Toe
The most noticeable symptom is a continuous ache or pain in the ball of the foot, directly beneath the big toe. Initially mild, this discomfort often intensifies with activities that exert pressure on the forefoot, such as walking, running, or jumping.
Visible Swelling and Bruising
The area around the sesamoid bones may exhibit signs of swelling or bruising, indicating inflammation and serving as a visible marker of the condition.
Impaired Toe Movement
Sesamoiditis can hinder the flexibility of the big toe, making movements like bending or straightening the toe painful and challenging, thereby affecting your gait and foot function.
Warmth and Sensitivity
The affected area might feel unusually warm or tender to the touch, suggesting inflammation and differentiating sesamoiditis from other foot-related issues.
Discomfort with Certain Footwear or When Walking Barefoot
Pain may escalate when wearing shoes that lack adequate support or have elevated heels. Similarly, walking barefoot on hard surfaces might increase the pain due to the absence of cushioning and support.
Path to Diagnosis and Healing
Diagnosis
Comprehensive Foot Examination: The diagnostic process begins with a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, focusing on the foot’s structure, pinpointing the precise pain location, and identifying exacerbating activities.
Utilization of Imaging Tests: To confirm the diagnosis of sesamoiditis and rule out other conditions such as fractures, imaging studies are often employed, including:
- X-rays: These images highlight bone structure and can reveal abnormalities or changes in the sesamoid bones.
- MRIs: Offering detailed views of both bone and soft tissue, MRIs are crucial for assessing the extent of inflammation around the sesamoid bones and confirming the diagnosis.
Effective Treatment Strategies
Upon diagnosing sesamoiditis, the focus shifts to alleviating discomfort, reducing inflammation, and addressing any contributing factors. A holistic treatment plan typically includes several strategies:
- Rest and Cold Therapy: Taking a break from activities that place undue stress on the foot and applying cold packs can significantly reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Pressure Redistribution: Using cushioned pads or custom orthotic inserts helps shift pressure away from the sesamoid bones, providing relief.
- Appropriate Footwear: Shoes with a supportive arch, low heel, and roomy toe box can minimize pressure on the sesamoid area. High heels and tight shoes should be avoided in favor of options that offer better cushioning and support.
- Anti-inflammatory Medication: NSAIDs can be effective in managing pain and reducing inflammation, providing temporary relief from symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises designed to strengthen the muscles around the big toe and improve foot mechanics can help ease discomfort and prevent future issues.
- Foot Immobilization: For cases where less invasive treatments don’t provide relief, immobilizing the foot with a brace or cast may be necessary to allow for healing.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgery may be required to remove one of the sesamoid bones or repair damaged tendons if conservative treatments prove ineffective.
Prevention Tips
Choose the Right Shoes
Selecting footwear that offers adequate support and comfort is crucial, especially for those engaging in high-impact activities. Shoes with narrow toe boxes should be avoided.
Strengthening Exercises
Regularly performing exercises that strengthen the foot muscles can help maintain arch health and prevent sesamoiditis. Activities like toe curls, marble pickups, and arch lifts are recommended.
Weight Management
Keeping a healthy weight can reduce the pressure and stress on the sesamoid bones, mitigating the risk of developing sesamoiditis.
Regular Stretching
Flexibility in the feet, ankles, and calves can be improved with consistent stretching, decreasing the likelihood of injuries that could lead to sesamoiditis.
The Path to Recovery
| Early Detection: Recognizing the symptoms early on is crucial for effective management. Symptoms to watch for include pain in the forefoot, swelling, or difficulty in toe movement. |
| Seek Professional Help: If you suspect sesamoiditis or experience persistent foot pain, consulting a healthcare professional early can prevent the condition from worsening and facilitate a quicker recovery. |
| Educate and Prevent: Being informed about the causes, risk factors, and preventive measures for sesamoiditis empowers individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining foot health, both for themselves and within their communities. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What exactly is Sesamoiditis?
A: Sesamoiditis is inflammation and pain in the area beneath the big toe, caused by stress on the sesamoid bones, crucial for foot mechanics.
Q: What activities increase the risk of developing Sesamoiditis?
A: High-impact sports, ballet dancing, and occupations requiring prolonged standing or walking can elevate the risk.
Q: How can I tell if I have Sesamoiditis?
A: Key symptoms include persistent pain under the big toe, swelling, bruising, impaired toe movement, and discomfort with certain footwear or walking barefoot.
Q: What are the most effective treatment strategies for Sesamoiditis?
A: Treatments include rest, cold therapy, pressure redistribution with orthotic inserts, appropriate footwear, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, and possibly surgery in severe cases.
Q: Can it be prevented?
A: Yes, by choosing the right shoes, engaging in foot-strengthening exercises, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular stretching.
Conclusion
Sesamoiditis, while challenging, is not insurmountable. With early detection, professional guidance, and adherence to recommended treatment and prevention strategies, individuals can navigate the path to recovery and regain their foot health. Empower yourself with knowledge and proactive measures to protect your feet, ensuring a future free from the discomfort of Sesamoiditis. Remember, your journey to recovery begins with understanding and taking the first step towards effective management and prevention.
MOST COMMENTED
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Is Protein Powder Safe for Teenagers and Children?
Animal-Based Proteins / Casein Protein / Dietary Protein / High-Protein Diets / Pea Protein / Plant-Based Proteins / Protein / Protein Deficiency / Protein Supplements / Proteins / Whey Protein / Whey Proteins
Unlock the Power of Proteins for Optimal Gut Health
Multivitamin
Total Health: Multivitamin for Active Lifestyles
Multivitamin
WellnessFusion: Complete Multivitamin Support
Dietary Supplement
Revitalize Your Health: The Magic of Red Yeast Rice Capsules
Foot care / Foot Health
Revitalize Your Foot Care Routine: Essential Tips for Optimal Foot Health
Foot Problem / Diabetics / Foot Health
Diabetics: Mastering Footwear Selection for Enhanced Foot Health and Ultimate Comfort
Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief / Foot care / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem / Hammertoes
Unlock Effective Exercises and Footwear Tips for Hammertoe Relief
Hammertoes / Foot Health / Foot Pain / Foot Problem
Unlock Relief: Essential Guide to Hammertoes Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Foot Problem / Foot Health
Revolutionize Your Recovery: Natural Remedies for Plantar Fasciitis – Fresh Home Keepers